上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
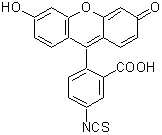
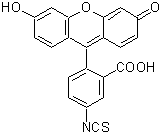
C21H11NO5S
389.38
关联产品

上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
C21H11NO5S
389.38
关联产品

DAKO C4c Complement FITC标记现货供应
DAKO C4c Complement FITC标记现货供应
Polyclonal Rabbit
Anti-Human
C4c Complement/FITC
Code No./ Code/ Code-Nr. F 0169
DAKO抗体是丹麦的著名抗体生产商,提供世界上质量zui稳定,zui为经典的抗体。其主要产品涉及免疫化学、流式细胞,免疫组织化学,原位杂交,微生物检验等。DAKO的不同显色系统,Envision,LSAB和免疫细胞化学的CAS,GenpointTM和用于分子病理学的PNA=ISH试剂盒,和用于ELISA的AMPAKTM/AmpliQ是其在生物化学研究中的革新产品 。
Intended use For in vitro diagnostic use.
F 0169 is intended for the demonstration of complement C4, C4b and C4c in tissue sections, and may also be used for
other immunofluorescence techniques. Interpretation of results must be made within the context of the patient’s clinical
history and other diagnostic tests by a certified professional.
丹科DAKO兔抗人IgA/FITC标记二抗,Polyclonal Rabbit Anti-Human
丹科DAKO兔抗人IgA/FITC标记二抗,Polyclonal Rabbit Anti-Human IgA
货号:F020402-2
规格:2ml
现货供应中
丹科DAKO兔抗人IgA/FITC标记二抗,Polyclonal Rabbit Anti-Human IgA
简介:
For use in methods demanding a very high specificity. The specificity and performance of the antibody have been ascertained in immunohistochemistry and ELISA. Additionally, the specificity has been tested by crossed immunoelectrophoresis using 12.5 microlitre antibody per square cm gel area against 2 microlitre human plasma. The antigen used for immunization is serum IgA.
The F(ab')2 fragment antibody is particularly useful for labeling unfixed blood cells containing active Fc receptors, and for other applications where the Fc part of the antibody molecule could disturb.
Please note that F(ab')2 fragment antibodies are not suited for techniques dependant on aggregation or precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes.
详细产品信息可咨询我公司销售人员
DAKO(丹科)兔抗人IgM/FITC标记,Rb a Hu IgM/FITC
DAKO(丹科)兔抗人IgM/FITC标记,Rb a Hu IgM/FITC
英文名:Polyclonal Rabbit Anti-Human IgM/FITC
规格:2ml
For use in methods demanding a very high specificity. The specificity and performance of the antibody have been ascertained in immunohistochemistry and ELISA. Additionally, the specificity has been tested by crossed immunoelectrophoresis using 12.5 microlitre antibody per square cm gel area against 2 microlitre human plasma.
The F(ab')2 fragment antibody is particularly useful for labeling unfixed blood cells containing active Fc receptors, and for other applications where the Fc part of the antibody molecule could disturb.
Please note that F(ab')2 fragment antibodies are not suited for techniques dependant on aggregation or precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes.
DAKO(丹科)兔抗人IgM/FITC标记,Rb a Hu IgM/FITC
DAKO抗体是丹麦的著名抗体生产商,提供世界上质量zui稳定,zui为经典的抗体。其主要产品涉及免疫化学、流式细胞,免疫组织化学,原位杂交,微生物检验等。DAKO的不同显色系统,Envision,LSAB和免疫细胞化学的CAS,GenpointTM和用于分子病理学的PNA=ISH试剂盒,和用于ELISA的AMPAKTM/AmpliQ是其在生物化学研究中的革新产品 。
详细产品信息可
BD细胞凋亡试剂盒(FITC标记)FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detectio
BD细胞凋亡试剂盒(FITC标记)FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I
现货*
Technical Data Sheet
FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I
Product Information
Material Number: 556547
Component: 51-66121E
Description: 10X Annexin V Binding Buffer
Size: 50 ml (1 ea)
Storage Buffer: Aqueous buffered solution containing no preservative.
Component: 51-65874X
Description: FITC Annexin V
Size: 0.5 ml (1 ea)
Vol. per Test: 5 μl
Storage Buffer: Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA and ≤0.09% sodium azide.
Component: 51-66211E
Description: Propidium Iodide Staining Solution
Size: 2.0 ml (1 ea)
Vol. per Test: 5 μl
Storage Buffer: Aqueous buffered solution containing no preservative.
Description
Apoptosis is a normal physiologic process which occurs during embryonic development as well as in maintenence of tissue homeostasis. The
apoptotic program is characterized by certain morphologic features, including loss of plasma membrane asymmetry and attachment,
condensation of the cytoplasm and nucleus, and internucleosomal cleavage of DNA. Loss of plasma membrane is one of the earliest features.
In apoptotic cells, the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) is translocated from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma
membrane, thereby exposing PS to the external cellular environment. Annexin V is a 35-36 kDa Ca2+ dependent phospholipid-binding
protein that has a high affinity for PS, and binds to cells with exposed PS. Annexin V may be conjugated to fluorochromes including FITC.
This format retains its high affinity for PS and thus serves as a sensitive probe for flow cytometric analysis of cells that are undergoing
apoptosis. Since externalization of PS occurs in the earlier stages of apoptosis, FITC Annexin V staining can identify apoptosis at an earlier
stage than assays based on nuclear changes such as DNA fragmentation.
FITC Annexin V staining precedes the loss of membrane integrity which accompanies the latest stages of cell death resulting from either
apoptotic or necrotic processes. Therefore, staining with FITC Annexin V is typically used in conjunction with a vital dye such as propidium
iodide (PI) or 7-Amino-Actinomycin (7-AAD) to allow the investigator to identify early apoptotic cells (PI negative, FITC Annexin V
positive). Viable cells with intact membranes exclude PI, wheras the membranes of dead and damaged cells are permeable to PI. For example,
cells that are considered viable are FITC Annexin V and PI negative; cells that are in early apoptosis are FITC Annexin V positive and PI
negative; and cells that are in late apoptosis or already dead are are both FITC Annexin V and PI positive. This assay does not distinguish
between cells that have undergone apoptotic death versus those that have died as a result of a necrotic pathway because in either case, the dead
cells will stain with both FITC Annexin V and PI. However, when apoptosis is measured over time, cells can be often tracked from FITC
Annexin V and PI negative (viable, or no measurable apoptosis), to FITC Annexin V positive and PI negative (early apoptosis, membrane
integrity is present) and finally to FITC Annexin V and PI positive (end stage apoptosis and death). The movement of cells through these three
stages suggests apoptosis. In contrast, a single observation indicating that cells are both FITC Annexin V and PI positive, in of itself, reveals
less information about the process by which the cells underwent their demise.
Preparation and Storage
Store undiluted at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
556547 Rev. 5 Page 1 of 3
Flow Cytometric Analysis of FITC Annexin V staining. Jurkat cells
(Human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152) were left untreated (top
panels) or treated for 4 hours with 12 μM campotothecin (bottom
panels). Cells were incubated with FITC Annexin V in a buffer
containing propidium iodide (PI) and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Untreated cells were primarily FITC Annexin V and PI negative,
indicating that they were viable and not undergoing apoptosis. After a
4 hour treatment (bottom panels), there were primarily two
populations of cells: Cells that were viable and not undergoing
apoptosis (FITC Annexin V and PI negative) and cells undergoing
apoptosis (FITC Annexin V positive and PI negative). A minor
population of cells were observed to be FITC Annexin V and PI
positive, indicating that they were in end stage apoptosis or already
dead.
Application Notes
Application
Flow cytometry Routinely Tested
Recommended Assay Procedure:
FITC Annexin V is a sensitive probe for identifying apoptotic cells, binding to negatively charged phospholipid surfaces (Kd of ~5 x 10^-2) with
a higher affinity for phosphatidylserine (PS) than most other phospholipids. FITC Annexin V binding is calcium dependent and defined calcium
and salt concentrations are required for optimal staining as described in the FITC Annexin V Staining Protocol. Investigators should note that
FITC Annexin V flow cytometric analysis on adherent cell types (e.g HeLa, NIH 3T3, etc.) is not routinely tested as specific membrane
damage may occur during cell detachment or harvesting. Methods for utilizing Annexin V for flow cytometry on adherent cell types,
however, have been previously reported (Casiola-Rosen et al. and van Engelend et al.).
INDUCTION OF APOPTOSIS BY CAMPTOTHECIN
The following protocol is provided as an illustration on how FITC Annexin V may be used on a cell line (Jurkat).
BD细胞凋亡试剂盒(FITC标记)FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I
Materials
1. Prepare Camptothecin stock solution (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. C-9911): 1 mM in DMSO.
2. Jurkat T cells (ATCC TIB-152).
Procedure
1. Add Camptothecin (final conc. 4-6 μM) to 1 x 10^6 Jurkat cells.
2. Incubate the cells for 4-6 hr at 37°C.
3. Proceed with the FITC Annexin V Staining Protocol to measure apoptosis.
FITC ANNEXIN V STAINING PROTOCOL
FITC Annexin V is used to quantitatively determine the percentage of cells within a population that are actively undergoing apoptosis. It relies on
the property of cells to lose membrane asymmetry in the early phases of apoptosis. In apoptotic cells, the membrane phospholipid
phosphatidylserine (PS) is translocated from the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane to the outer leaflet, thereby exposing PS to the external
environment. Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein that has a high affinity for PS, and is useful for identifying
apoptotic cells with exposed PS. Propidium Iodide (PI) is a standard flow cytometric viability probe and is used to distinguish viable from
nonviable cells. Viable cells with intact membranes exclude PI, whereas the membranes of dead and damaged cells are permeable to PI. Cells that
stain positive for FITC Annexin V and negative for PI are undergoing apoptosis. Cells that stain positive for both FITC Annexin V and PI are
either in the end stage of apoptosis, are undergoing necrosis, or are already dead. Cells that stain negative for both FITC Annexin V and PI are
alive and not undergoing measurable apoptosis.
556547 Rev. 5 Page 2 of 3
Reagents
1. FITC Annexin V (component no. 51-65874X): Use 5 μl per test.
2. Propidium Iodide (PI) (component no. 51-66211E) is a convenient, ready-to-use nucleic acid dye. Use 5 μl per test.
3. 10X Annexin V Binding Buffer (component no. 51-66121E): 0.1 M Hepes/NaOH (pH 7.4), 1.4 M NaCl, 25 mM CaCl2. For a 1X working
solution, dilute 1 part of the 10X Annexin V Binding Buffer to 9 parts of distilled water.
Staining
1. Wash cells twice with cold PBS and then resuspend cells in 1X Binding Buffer at a concentration of 1 x 10^6 cells/ml.
2. Transfer 100 μl of the solution (1 x 10^5 cells) to a 5 ml culture tube.
3. Add 5 μl of FITC Annexin V and 5 μl PI.
4. Gently vortex the cells and incubate for 15 min at RT (25°C) in the dark.
5. Add 400 μl of 1X Binding Buffer to each tube. Analyze by flow cytometry within 1 hr.
SUGGESTED CONTROLS FOR SETTING UP FLOW CYTOMETRY
The following controls are used to set up compensation and quadrants:
1. Unstained cells.
2. Cells stained with FITC Annexin V (no PI).
3. Cells stained with PI (no FITC Annexin V).
Other Staining Controls:
A cell line that can be easily induced to undergo apoptosis should be used to obtain positive control staining with FITC Annexin V and/or FITC
Annexin V and PI. It is important to note that the basal level of apoptosis and necrosis varies considerably within a population. Thus, even in the
absence of induced apoptosis, most cell populations will contain a minor percentage of cells that are positive for apoptosis (FITC Annexin V
positive, PI negative or FITC Annexin V positive, PI positive).
The untreated population is used to define the basal level of apoptotic and dead cells. The percentage of cells that have been induced to undergo
apoptosis is then determined by subtracting the percentage of apoptotic cells in the untreated population from percentage of apoptotic cells in the
treated population. Since cell death is the eventual outcome of cells undergoing apoptosis, cells in the late stages of apoptosis will have a damaged
membrane and stain positive for PI as well as for FITC Annexin V. Thus the assay does not distinguish between cells that have already undergone
an apoptotic cell death and those that have died as a result of necrotic pathway, because in either case the dead cells will stain with both FITC
Annexin V and PI.
Product Notices
1. Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
2. Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before
discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
3.
4. Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols for technical protocols.
References
Andree HA, Reuingsperger CP, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC, Hermens WT, Willems GM. Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha (VAC alpha) to planar
phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265(9):4923-4928. (Biology)
Casciola-Rosen L, Rosen A, Petri M, Schlissel M. Surface blebs on apoptotic cells are sites of enhanced procoagulant activity: implications for coagulation events
and antigenic spread in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93(4):1624-1629. (Biology)
Homburg CH, de Haas M, von dem Borne AE, Verhoeven AJ, Reuingsperger CP, Roos D. Human neutrophils lose their surface Fc gamma RIII and acquire
Annexin V binding sites during apoptosis in vitro. Blood. 1995; 85(2):532-540. (Biology)
Koopman G, Reuingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH. Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on
B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood. 1994; 84(5):1415-1420. (Biology)
Martin SJ, Reuingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of
the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med. 1995; 182(5):1545-1556. (Biology)
O’Brien MC, Bolton WE. Comparison of cell viability probes compatible with fixation and permeabilization for combined surface and intracellular staining in flow
cytometry. Cytometry. 1995; 19(3):243-255. (Biology)
Raynal P, Pollard HB. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994; 1197(1):63-93. (Biology)
Schmid I, Krall WJ, Uittenbogaart CH, Braun J, Giorgi JV. Dead cell discrimination with 7-amino-actinomycin D in combination with dual color immunofluorescence
in single laser flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992; 13(2):204-208. (Biology)
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reuingsperger CP. A novel assay to measure loss of plasma membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent
cells in culture. Cytometry. 1996; 24(2):131-139. (Biology)
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reuingsperger C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early
apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 1995; 184(1):39-51. (Biology)
n Kit I详细产品信息可和选购
FITC标记细胞凋亡检测试剂盒Annexin V-FITC
FITC标记细胞凋亡检测试剂盒Annexin V-FITC(Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit)是用FITC标记的重组人Annexin V来检测细胞凋亡时出现在细胞膜表面的磷酯酰丝氨酸的一种细胞凋亡检测试剂盒。可以使用流式细胞仪、荧光显微镜或其它荧光检测设备进行检测。
Annexin是一类广泛分布于真核细胞细胞浆内钙离子依赖的磷酯结合蛋白,参与细胞内的信号转导。但仅Annexin V被报道可以调控一些PKC的活性。
FITC标记细胞凋亡检测试剂盒Annexin V-FITC
Annexin V选择性结合磷酯酰丝氨酸(phosphatidylserine,简称PS)。磷酯酰丝氨酸主要分布在细胞膜内侧,即与细胞浆相邻的一侧。在细胞发生凋亡的早期,不同类型的细胞都会把磷酯酰丝氨酸外翻到细胞表面,即细胞膜外侧。磷酯酰丝氨酸暴露到细胞表面后会促进凝血和炎症反应。而Annexin V和外翻到细胞表面的磷酯酰丝氨酸结合后可以阻断磷酯酰丝氨酸的促凝血和促炎症反应活性。
用带有绿色荧光的荧光探针FITC标记的Annexin V,即Annexin V-FITC,就可以用流式细胞仪或荧光显微镜非常简单而直接地检测到磷酯酰丝氨酸的外翻这一细胞凋亡的重要特征。
本试剂盒还提供了碘化丙啶染色液,碘化丙啶可以染色坏死细胞或凋亡晚期丧失细胞膜完整性的细胞,呈现红色荧光。对于坏死细胞,由于细胞膜的完整性已经丧失,Annexin V-FITC可以进入到细胞浆内,与位于细胞膜内侧的磷酯酰丝氨酸结合,从而也使坏死细胞呈现绿色荧光。
综上所述,参考下图,用Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶染色后,正常的活细胞不被Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶染色(下图左下角);凋亡早期的细胞仅被Annexin V-FITC染色,碘化丙啶染色呈阴性(下图右下角);坏死细胞和凋亡晚期的细胞可以同时被Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶染色(下图右上角)。下图左上角出现的是许可范围内的检测误差。
包装清单:
|
产品编号 |
产品名称 |
包装 |
|
C1063-1 |
Annexin V-FITC |
250μl |
|
C1063-2 |
Annexin V-FITC结合液 |
26ml |
|
C1063-3 |
碘化丙啶染色液 |
550μl |
|
— |
说明书 |
1份 |
保存条件:
4℃保存,Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶染色液需避光保存,半年有效。为长期保存,可以把碘化丙啶染色液适当分装后-20℃保存,Annexin V-FITC结合液可以直接-20℃保存。
注意事项:
如果有细菌或真菌污染,会严重影响检测效果。
染色后宜尽快检测,时间过长可能会导致凋亡或坏死细胞的数量增加。
如果细胞收集过程中使用了胰酶,需注意设法去除残留的胰酶。残留的胰酶会消化并降解Annexin V-FITC,zui终导致染色失败。
荧光物质均易发生淬灭,在进行荧光观察时,尽量缩短观察时间,同时在操作和存放过程中也尽量注意避光保存。
需自备PBS。
为了您的安全和健康,请穿实验服并戴一次性手套操作。
详细产品信息可和选购
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学试剂盒全线产品,欢迎访问日本同仁化学dojindo官网了解更多信息。
| 容 量 | メーカー希望 小売価格 |
富士フイルム 和光純薬 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | ¥11,200 | 349-03661 |
| 500 mg | ¥37,200 | 343-03664 |


100 mg/10 mL(アセトン)
1) 川村明義, "蛍光抗体法(fluorescent antibody technique), 免疫の生化学", 共立出版, 1996.
2) H. Kawaguchi, K. Tuzimura, H. Maeda and N. Ishida, "Reaction of Fluorescein-isothiocyanate with Proteins and Amino Acids", J. Biochem., 1969, 66, 783.
3) H. Maeda, N. Ishida, H. Kawauchi and K. Tuzimura, "Reaction of Fluorescein-Isothiocyanate with Proteins and Amino Acids", J. Biochem., 1969, 65, 777.
4) W. B. Cherry, "Evaluation of Commercial Fluorescein Isothiocyanates Used in Fluorescent Antibody Studies", Stain Technology, 1969, 44, 179.
5) 川村明義, 和田計二, 浜島健治, 村田道里, "蛍光抗体法における観察法とその進歩", 臨床検査, 1973, 17, 28.
6) 村本光二, 目黒煕, "けい光によるペプチドの構造解析の超微量化の試み", ぶんせき, 1979, 821.
7) G. Radcliff, R. Waite, J. Lefevre, M. D. Poulik and D. M. Callewaert, "Quantification of Effector/Target Conjugation Involving Natural Killer(NK) or Lymphokine Activated Killer(LAK) Cells by Two-color Flow Cytometry", J. Immunol. Methods, 1991, 139, 281.
8) C. Souchier, M. Ffrench, M. Benchaib, R. Catallo and P. A. Bryon, "Methods for Cell Proloferation Analysis by Fluorescent Image Cytometry", Cytometry, 1995, 20, 203.
FITC-I を使用したタンパク質標識の方法を教えてください。
FITC-I による標識例を紹介致します。
この方法は次の書籍を参考としております。
・G. T. Hermanson, "Bioconjugate Techniques, Second Edition", Elsevier, 2008.
<FITC-I によるタンパク質標識例>
(1) 0.1 mol/L 炭酸バッファー (pH9.0)で、2 mg/mL以上の濃度のタンパク質溶液を調製する。
(2)FITC-Iをdry DMSOで溶解する(1 mg/mL)。
FITC溶液調製後は、アルミホイルで包むなどして遮光しておく。*1
(3)タンパク質溶液1 mLに対し、1 mg/mL FITC溶液を50~100 μL添加し、遮光下、4℃で8時間以上反応させる。*2
(4)反応後 Sephadex G-25等のゲル濾過カラムを使ってPBSで溶離し、精製する。


| 性状: | 本品は、黄橙色粉末である。 |
|---|---|
| 純度(HPLC): | 95.0% 以上 |
| アセトン溶状: | 試験適合 |
| モル吸光係数: | 80,000 以上(492 nm付近) |
| IRスペクトル: | 試験適合 |
| 保存条件: 冷蔵 |
