上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
关联产品

实验工具|稀释计算器|摩尔浓度计算器

上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
关联产品



实验工具|稀释计算器|摩尔浓度计算器
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息

试剂盒内含

产品概述
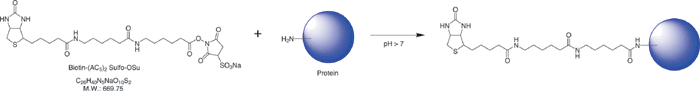
水溶性活性酯型生物素化试剂:使用生物素(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu用于生物素标记蛋白质游离氨基的试剂盒。它带有用于标记的LVDS3缓冲粉,用于凝胶过滤的柱和用于柱洗脱的PBS片剂,可以纯化标记的蛋白。由于是单次注射型(10毫克x4瓶),因此可以标记4种不同类型的蛋白质。可以通过改变添加的生物素-(AC5)2 Sulfo-OSu的量来控制标记率。
*标记蛋白的量为1-5 mg。
原理
操作步骤
使用注意事项:
1. 本试剂盒请在0-5 ℃储存。
2. Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu溶液需要现配现用 (由于Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu易水解,尽量避免在水溶液的状态保存)。
3. 标记好的蛋白质请在0-5 ℃保存 (加入0.1%的叠氮钠等防腐剂)。
使用步骤:
1. 配制溶液
1) NaHCO3缓冲液
在含有NaHCO3粉末的容器中加入10ml超纯水溶解。
2) PBS缓冲液
在100ml容量瓶中加入1片PBS,先用少量超纯水溶解后,再用超纯水补充至100ml,制成10mmol/l的PBS缓冲液。
3) 蛋白质溶液
在样品管中精确称量1.0-5.0mg蛋白质并记录称量值后,用移液器加入500μl操作步骤1)中的NaHCO3缓冲液。盖上盖子后,用漩涡振荡器等搅拌溶解蛋白质。
4) Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu溶液
在1支含有Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu的管子中加入适量纯水溶解。为了控制标记率,根据不同的标记对象,请参考表1调整Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu溶液的浓度及加入量。
*由于Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu易水解,溶解后请尽快标记。
2. 生物素标记操作方法
1) 请参考表1在配制好的蛋白质溶液中加入合适浓度和用量的Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu溶液。
2) 盖紧盖子充分混合后,在25 ℃水浴恒温摇床中培养2h。
表1 Biotin-(AC5)2Sulfo-OSu标记各种蛋白质的标记率
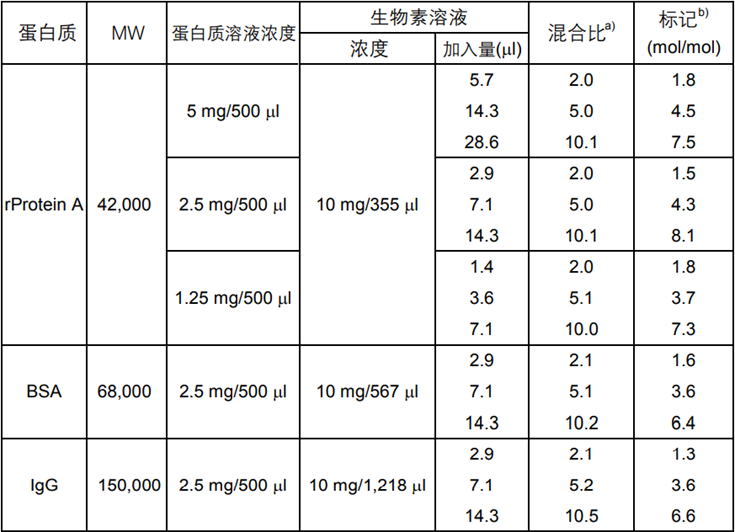
以上数据为本公司实际检测的结果,如实验条件变动,
结果有可能改变。标记率是根据HABA法测得。
a) 1mol蛋白质:生物素的摩尔数
b) 1mol蛋白质上所结合的生物素的摩尔数
3. 蛋白质标记后的凝胶过滤纯化
1) 打开层析柱上的盖子,弃去填充液。
2) 打开层析柱出口的盖子,用PBS分数次洗脱,每根层析柱收集大约10ml的洗脱液,使凝胶平衡。
3) 用移液器吸取500μl标记好的蛋白质溶液加入到层析柱中,弃去此时的流出液。
4) 在层析柱的出口处放置一个2ml的样品管,在层析柱中加入1ml PBS,收集流出的生物素标记蛋白质。
*经过层析,生物素标记蛋白质的最终浓度为标记时的1/2。
按照下列公式计算生物素标记蛋白质的最终浓度:
A (mol/l) = (X/MWprotein) × (1,000/Y) × 0.5
X:蛋白质的重量
MWprotein:蛋白质的分子量
Y:溶解蛋白质的NaHCO3缓冲液体积
常见问题Q&A
| Q1:如何存储标记的蛋白质? |
| A:将标记的蛋白质存放在冰箱中。另外,添加0.1%叠氮化钠作为防腐剂。 |
| Q2:生物素标记试剂在水溶液中稳定吗? |
| A:试剂盒中使用的生物素-(AC5)2 Slufo-OSu处于水溶液中时,由于它会水解,因此无法存储在水溶液中。使用前请做好准备。另外,即使在粉末状态下,也要注意由于吸湿引起的劣化。 |
参考文献
| 1) J. Wormmeester, F. Stiekema and C. Groot, “Immunoselective Cell Separation”, Methods Enzymol., 1990, 184, 314. |
| 2) J. J. Leary and D. J. Ward, “Rapid and Sensitive Colorimetric Method for Visualizing Biotin-labeled DNA Probes Hybridized to DNA or RNA Immoilized on Nitrocelulose: Bio-blots”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1983, 80, 4045. |
| 3) W. T. Lee and D. H. Conrad, “The Murine Lymphocyte Receptor for IgE II. Characterization of the Multvalent Nature of the B Lymphocyte Receptor for IgE”, J. Exp. Med., 1984, 159, 1790. |
| 4) D. R. Gretch, M. Suter and M. F. Stinski, “The Use of Biotinylated Monoclonal Antibodies and Streptavidin Affinity Chromatography to Isolate Herpesvirus Hydorophobic Proteins or Glycoproteins”, Anal. Biochem., 1987, 163, 270. |
| 5) M. Shimkus, J. Levy and T. Herman, “A Chemically Cleavable Biotinylated Nucleotide: Usefulness in the Recovery of Protein-DNA Complexes from Avidin Affinity Columns”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1985, 82, 2593. |
| 6) W. J. LaRochelle and S. C. Froehner, “Immunodhemical Detection of Proteins Biotinylated on Nitrocellulose Replicas”, J. Immunol. Methods, 1986, 92, 65. |
| 7) P. S. Anjaneyulu and J. V. Staros,”Reactions of N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide Active Esters”, Int. J. Pept. Protein Res., 1987, 30, 117. |
| 8) H. M. Ingalls, C. M. Goodloe-Holland and E. J. Luna,”Junctional Plasma Membrane Domains Isolated from Aggregating Dictyostelium Discoideum Amebae”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1986, 83, 4779. |
| 9) J. Guesdon, T. Ternyck and S. Avrameas,”The Use of Avidin-Biotin Interaction in Immunoenzymatic Techniques”, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 1979, 27, 1131. |
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
关联产品
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
特点:
● 整个标记过程仅需3个小时
● 整个标记过程在1支过滤管中进行
● 荧光标记抗体回收率高
● 适用于50-200 μg的IgG


试剂盒内含

产品概述
生物素标记试剂盒-SH是用于在具有SH基团的蛋白质(尤其是抗体)上标记生物素的试剂盒。由于试剂盒中包含的SH反应性生物素分子中具有马来酰亚胺基团,因此仅通过与具有SH基团的分子混合即可形成稳定的共价键。如果蛋白质具有S-S键,则可以使用连接的还原剂制备游离的SH基团。(但是,由于SS键的断裂,蛋白质的活性可能会丢失。)当用生物素标记高分子量蛋白质(例如免疫球蛋白G(IgG))时,可以使用所附的过滤管轻松进行预采样。如果可以进行处理并且将铰链区中的SH基团用于标记,则可以制备生物素标记的还原IgG,而不会损害抗体活性。另外,未反应的SH-反应性生物素可以在反应后通过使用滤管的纯化操作除去。
原理
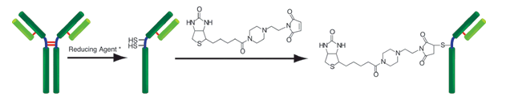
操作步骤
使用注意事项:
1. 用该试剂盒标记的蛋白质的分子量要>50,000。
2. 在标记过程中,IgG或者Biotin-IgG标记物始终存在于过滤管的滤膜上。
3. 如果蛋白质溶液中含有分子量>10,000的其他蛋白质,如BSA或明胶时,在使用该试剂盒标记前,先要纯化IgG溶液。IgG溶液能够用IgG Purification Kits (不包含于本试剂盒中) 来纯化。
4. 如果蛋白质溶液含有小的不溶物,离心后取上清液来进行标记。
5. 1管SH-Reactive Biotin可以标记50-200ug蛋白质。
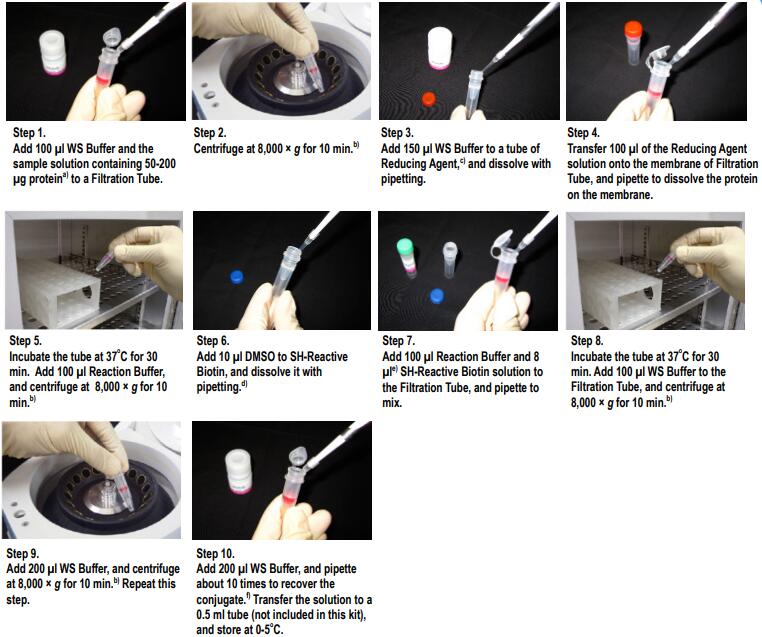
标记IgG操作步骤
(1)将100μl WS buffer以及含有100μg IgG的样品溶液加入到过滤管中。a)
(2)8,000-10,000g离心10分钟。b)
(3)将150μl WS buffer加入到Reducing agent管中,并用移液器吹打使其溶解。
(4)将100μl Reducing agent溶液转移到过滤管的滤膜上,吹打使IgG在膜上溶解。
(5)37℃培养30分钟。加入100μl Reaction buffer,8,000-10,000g离心10分钟。b)
(6)将10μl DMSO加入到SH-reactive biotin中,吹打使其溶解。c)
(7)将100μl Reaction buffer与8μl SH-reactive biotin溶液加入到过滤管中,吹打使其混合。d)
(8)37℃培养30分钟。将100μl WS buffer加入到过滤管中8,000-10,000g离心10分钟。 b)
(9)加入200μl WS buffer,8,000-10,000g离心10分钟。b)再重复该步骤一次。
(10)加入200μl WS buffer,吹打10-15次来回收标记产物。e)将该溶液转移到0.5ml试管中,在0-5℃下保存。
a) 样品溶液的体积不应超过100ul。如果蛋白质浓度<0.5mg/ml,重复操作步骤1和2直至总的IgG聚积量达到100ug。如果聚积过程中滤液的体积超过400 ul,则在进行后续的离心操作前应除去滤液。
b) 如果溶液在离心后仍然残留在膜上,可以再离心5min或者适当增加转速直至膜上没有残留液体。
c) NH2-Reactive Biotin/SH-Reactive Biotin在管子的底部,向管底加入10ul DMSO,吹打数次使其溶解。
d) 如果IgG的量为200ug,在步骤4时加入所有的NH2-ReactiveBiotin溶液。
e) 并不一定要使用WS Buffer来回收标记产物,可以选择任何适合于该实验的缓冲液来替代。
产品优势
1、整个标记过程仅需3个小时
2、整个标记过程在1支过滤管中进行
3、荧光标记抗体回收率高
4、适用于50-200 μg的IgG
常见问题Q&A
| Q1:样品溶液中的共存会影响反应吗? |
| A:它可能会受到共存类型的影响。确认溶液中包含哪种物质后,根据情况纯化用于标记的蛋白质,并将其用于标记反应。<聚合物:分子量10,000以上>它可能会影响。即使使用Filtration Tube,也无法去除具有氨基的高分子量化合物,例如BSA和明胶。因此,它被标记并充当荧光杂质。 在反应中使用之前,请执行单独的清除操作。另一方面,如果存在许多高分子杂质,即使没有氨基的化合物也可能导致过滤器堵塞。它可能会干扰标记/纯化操作。 *不仅对于生物素标记试剂盒-SH,而且对于其他标记试剂盒,都需要采取相同的预防措施。 |
| Q2:标记小分子蛋白质(分子量50,000或以下)的方法。 |
| A:由于该试剂盒中包含的过滤管是分子量截断值为30K的超滤过滤器,因此我们建议使用50,000或分子量更大的蛋白质,并留有余量。当标记分子量为50,000或更小的蛋白质时,可以通过更换为分子量分数较小的超滤过滤器来标记甚至很小的蛋白质,如下所示。
—————————————— PALL Nanocep 3K产品编号OD003C33 PALL Nanocep 10K产品编号OD010C33 —————————————— 离心所需的时间可能比试剂盒中随附的过滤器要长,因此请注意离心时间。 |
| Q3:标记后,离心过滤管,液体仍会留在膜上怎么处理? |
| A:(1)目视检查隔膜时,如果液体稍微残留在隔膜杯的边缘,请继续执行下面操作。如果倾斜和旋转膜杯时液体残留在膜上或滴下,请以8,000 g离心约15至30分钟。 (2)即使在1)中的离心操作之后,如果液体仍留在膜上,请检查标记物质是否聚集。
根据抗体或蛋白质本身的特性,用小分子标记剂进行标记可能会增加抗体或蛋白质的疏水性并使其聚集。如果在标记的物质上观察到团聚,将其转移到另一个微管中一次,离心并使用上清液。 (回收的抗体/蛋白质的量将减少。)如果上述方法没有帮助,请与公司技术支持联系。 *如果您怀疑过滤器堵塞,可以通过更换新的膜过滤器来解决。 替代品:PALL Nanocep 30K(制造商代码:OD030C33) |
| Q4:该试剂盒可以标记什么? |
| A:可以标记分子量为“50,000或更高”并且具有[S-S]或[SH]的任何化合物(抗体,蛋白质等)。量为“50-200μg”。 *由于试剂盒中包含的过滤管尺寸为30K,因此无法纯化低分子量化合物。 |
参考文献
1) E. Terasaka, K. Yamada, P.H. Wang, K. Hosokawa, R. Yamagiwa, K. Matsumoto, S. Ishii, T. Mori, K. Yagi, H. Sawai, H. Arai, H. Sugimoto, Y. Sugita, Y. Shiro and T. Tosha, “Dynamics of nitric oxide controlled by protein complex in bacterial system”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.., 2017, 114, (37), 9888.
2) J. Hiruma, K. Harada, A. Motoyama, Y. Okubo, T. Maeda, M. Yamamoto, M. Miyai, T. Hibino and R. Tsuboi, “Key component of inflammasome, NLRC4, was identified in the lesional epidermis of psoriatic patients”, J. Dermatol.., 2018, 45, (8), 971.
3) K. Gonda, M. Watanabe, H. Tada, M. Miyashita, Y. Takahashi-Aoyama, T. Kamei, T. Ishida, S. Usami, H. Hirakawa, Y. Kakugawa, Y. Hamanaka, R. Yoshida, A. Furuta, H. Okada, H. Goda, H. Negishi, K. Takanashi, M. Takahashi, Y. Ozaki, Y. Yoshihara, Y. Nakano and N. Ohuchi, “Quantitative diagnostic imaging of cancer tissues by using phosphor-integrated dots with ultra-high brightness”, Sci. Rep.., 2017, 7, (1), 7509.
4) K. Saito, M. Sakaguchi, H. Iioka, M. Matsui, H. Nakanishi, N.H. Huh and E. Kondo, “Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor is a critical regulator for the survival and growth of oral squamous carcinoma cells”, Oncogene., 2014, 33, (10), 127401286.
5) K. Yamamoto, H. Murata, E.W. Putranto, K. Kataoka, A. Motoyama, T. Hibino, Y. Inoue, M. Sakaguchi and N.H. Huh, “DOCK7 is a critical regulator of the RAGE-Cdc42 signaling axis that induces formation of dendritic pseudopodia in human cancer cells”, Oncol. Rep.., 2013, 29, (3), 1073.
6) M. Sakaguchi, H. Murata, K. Yamamoto, T. Ono, Y. Sakaguchi, A. Motoyama, T. Hibino, K. Kataoka and N.H. Huh, “TIRAP, an Adaptor Protein for TLR2/4, Transduces a Signal from RAGE Phosphorylated upon Ligand Binding”, PLoS ONE., 2011, 6, (8), e23132.
7) M. Sakaguchi, H. Murata, Y. Aoyama, T. Hibino, E.W. Putranto, I.M. Ruma, Y. Inoue, Y. Sakaguchi, K. Yamamoto, R. Kinoshita, J. Futami, K. Kataoka, K. Iwatsuki and N.H. Huh, “DNAX-activating Protein 10 (DAP10) Membrane Adaptor Associates with Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) and Modulates the RAGE-triggered Signaling Pathway in Human Keratinocytes”, J. Biol. Chem.., 2014, 289, (34), 23389.
8) N. Kobayashi, K. Odaka, T. Uehara, K. Imanaka-Yoshida, Y. Kato, H. Oyama, H. Tadokoro, H. Akizawa, S. Tanada, M. Hiroe, T. Fukumura, I. Komuro, Y. Arano, T. Yoshida and T. Irie, “Toward in Vivo Imaging of Heart Disease Using a Radiolabeled Single-Chain Fv Fragment Targeting Tenascin-C”, Anal. Chem.., 2011, 83, (23), 9123.
9) T. Ikeda, R. Shinohata, M. Murakami, K. Hina, S. Kamikawa, S. Hirohata, S. Kusachi, A. Tamura and S. Usui, “A rapid and precise method for measuring plasma apoE-rich HDL using polyethylene glycol and cation-exchange chromatography: a pilot study on the clinical significance of apoE-rich HDL measurements”, Clin. Chim. Acta.,2017, 465, 112.
10) T. Into, M. Inomata, M. Nakashima, K. Shibata, H. Hacker and K. Matsushita, “Regulation of MyD88-Dependent Signaling Events by S Nitrosylation Retards Toll-Like Receptor Signal Transduction and Initiation of Acute-Phase Immune Responses”, Mol. Cell. Biol.., 2008, 28, (4), 1338.
11) W. Nakai, T. Yoshida, D. Diez, Y. Miyatake, T. Nishibu, N. Imawaka, K. Naruse, Y. Sadamura and R. Hanayama, “A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles”, Sci. Rep.., 2016, 6, 33935.
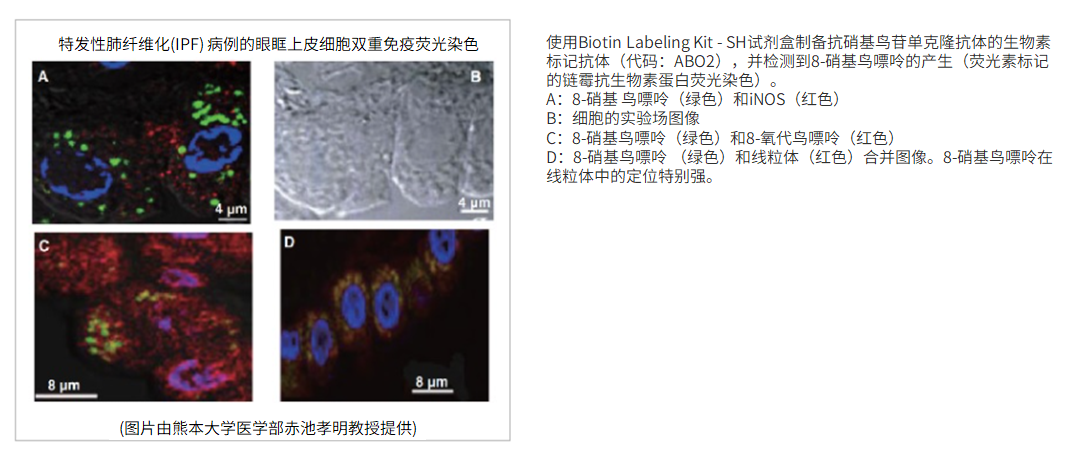
12) Y. Terasaki, T. Akuta, M. Terasaki, T. Sawa, T. Mori, T. Okamoto, M. Ozaki, M. Takeya and T. Akaike, “Guanine Nitration in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Its Implication for Carcinogenesis”, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.., 2006, 174, (6), 665.
13) I. W. Sumardika, C. Youyi, E. Kondo, Y. Inoue, I. M. W. Ruma, H. Murata, R. Kinoshita, K. Yamamoto, S. Tomida, K. Shien, H. Sato, A. Yamauchi, J. Futami, E. W. Putranto, T. Hibino, S. Toyooka , M. Nishibori and M. Sakaguchi, “β-1,3-Galactosyl-O-Glycosyl-Glycoprotein β-1,6-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 Increases MCAM Stability, Which Enhances S100A8/A9-Mediated Cancer Motility.”, Oncol. Res., 2018, 26, (3), 431.
14) J. Iwano, D. Shinmi, K. Masuda, T. Murakami and J. Enokizono, “Impact of Different Selectivity between Soluble and Membrane-bound Forms of Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) on the Target-mediated Disposition of Anti-CEA Monoclonal Antibodies.”, Drug Metab. Dispos., 2019, 47, (1), 1240.
15) D. S. On, P. Chertchinnapa, Y. Shinkai, T. Kojima and H. Nakano, “Development of a dual monoclonal antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of swine influenza virus using rabbit monoclonal antibody by Ecobody technology.”, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2020, DOI:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2020.03.003.
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息

活动进行中
订购满5000元,200元礼品等你拿
凑单关联产品TOP5
NO.1. Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2 生物素标记-氨基
NO.2. Cell Counting Kit-8 细胞增殖毒性检测
NO.3. Viability/Cytotoxicity Multiplex Assay Kit 细胞活性/毒性双重检测
NO.4. Fluorescein Labeling Kit – NH2 FITC(488激发)标记-氨基
NO.5. Biotin Labeling Kit – SH 生物素标记-巯基
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
特点:
● 生物素标记的产品可以在大约2小时内制备。
● 只需将NH2反应性生物素与目标蛋白混合即可形成稳定的共价键。
● 可以标记分子量为50,000或更高的蛋白质。
● 可以标记50-200μg的蛋白质。
● 可以通过使用过滤管的分离操作以高回收率获得标记物质。
● 生物素标记的产品可以与试剂盒中包含的存储溶液一起存储。

活动进行中
订购满5000元,200元礼品等你拿
凑单关联产品TOP5
NO.1. Cell Counting Kit-8 细胞增殖毒性检测
NO.2. Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST 乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)检测
NO.3. Fluorescein Labeling Kit – NH2 荧光素标记试剂盒-氨基
NO.4. Peroxidase Labeling Kit – NH2 过氧化物酶标记试剂盒-氨基
NO.5. Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2 (for 1mg) 生物素标记试剂盒-氨基
试剂盒内含

产品概述
生物素标记试剂盒-NH2是用于用生物素标记带有氨基基团的蛋白质的试剂盒,尤其是抗体,由于该试剂盒中包含的NH2-反应性生物素分子中具有活性酯基,因此仅通过与生物素混合即可形成稳定的共价键。当生物素标记在蛋白质(例如免疫球蛋白G(IgG))上时,可以使用随附的过滤管轻松去除抑制标记反应和未反应的NH2-反应性生物素的低分子量化合物(例如Tris)。因此,没有必要进行诸如透析和凝胶过滤的处理,并且可以以高回收率获得高纯度的标记化合物。
原理
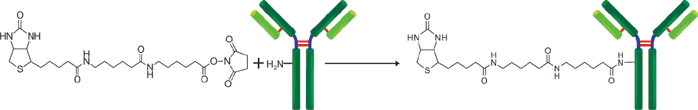
操作步骤
使用注意事项:
1. 用本试剂盒标记的蛋白质的分子量要>50,000。
2. 在标记过程中,IgG或者Biotin-IgG标记物始终存在于过滤管的滤膜上。
3. 如果IgG溶液中含有分子量>10,000的其他蛋白质,如BSA或明胶时,在使用该试剂盒标记前,先要纯化IgG溶液。IgG溶液能够用IgG Purification Kits (不包含于本试剂盒中) 来纯化。
4. 如果IgG溶液含有小的不溶物,离心后取上清液来进行标记。
5. 1管NH2-Reactive Biotin可以标记50-200 ug蛋白质。
标记IgG操作步骤
(1)将100μl WS buffer以及含有100μg IgG的样品溶液加入到过滤管中。a)
(2)8,000-10,000g离心10分钟。b)
(3)将10μl DMSO加入到NH2-reactive biotin中并用移液器吹打使其溶解。c)
(4)将100μl Reaction buffer以及8μl NH2-reactive biotin溶液加入到过滤管中,吹打使其混合。d)
(5)将过滤管放入培养箱中,37℃培养10分钟。
(6)将100μl WS buffer加入到过滤管中,8,000-10,000g离心10分钟,b)除去滤液。
(7)将200μl WS buffer加入到过滤管中,8,000-10,000g离心10分钟,b)重复该步骤一次。
(8)将200μl WS buffer加入到过滤管中吹打10-15次来回收标记产物。e)将该溶液转移到0.5ml试管中,在0-5℃下保存。

a) 样品溶液的体积不应超过100ul。如果蛋白质浓度低于0.5mg/ml,重复操作步骤1和2直至总的蛋白质聚积量达到50-200ug。如果聚积过程中滤液的体积超过400ul,则在进行后续的离心操作前应除去滤液。
b) 如果溶液在离心后仍然残留在膜上,可以再离心5min或者适当增加转速直至膜上没有残留液体。
c) NH2-Reactive Biotin在管子的底部,向管底加入10ul DMSO,吹打数次使其溶解。
d) 如果蛋白质的量为200ug,在操作步骤4时加入所有的NH2-Reactive Biotin-DMSO溶液。
e) 并不一定要使用WS Buffer来回收标记产物,可以选择任何适合于该实验的缓冲液来替代。
产品优势
1)生物素标记的产品可以在大约2小时内制备。
2)只需将NH2反应性生物素与目标蛋白混合即可形成稳定的共价键。
3)可以标记分子量为50,000或更高的蛋白质。
4)可以标记50-200μg的蛋白质。
5)可以通过使用过滤管的分离操作以高回收率获得标记物质。
6)生物素标记的产品可以与试剂盒中包含的存储溶液一起存储。
常见问题Q&A
| Q1:这个试剂盒可以用于标记其他蛋白质吗? |
| A:可以。但是如果含有像血清白蛋白或者明胶的蛋白,标记反应可能会受到干扰。用这个试剂盒标记之前,有必要先纯化抗体溶液。如果您想进一步了解纯化过程可以联系我们。 |
| Q2:我只有少量的IgG,可以标记吗? |
| A:在该试剂盒中,标记所需的IgG量为50至200μg。
在此范围内,性能没有太大差异。 可以用10μg IgG进行标记,但是可能会出现诸如背景升高的问题。 |
| Q3:样品溶液中的共存会影响反应吗? |
| A:它可能会受到共存类型的影响。确认溶液中包含哪种物质后,根据情况纯化用于标记的蛋白质,并将其用于标记反应。
<聚合物:分子量10,000以上>它可能会影响。即使使用Filtration Tube,也无法去除具有氨基的高分子量化合物,例如BSA和明胶。因此,它被标记并充当荧光杂质。 在反应中使用之前,请执行单独的清除操作。另一方面,如果存在许多高分子杂质,即使没有氨基的化合物也可能导致过滤器堵塞。它可能会干扰标记/纯化操作。 *生物素标记试剂盒-不仅需要对NH2采取相同的预防措施,还需要对其他标记试剂盒采取相同的预防措施。 |
| Q4:标记小分子蛋白质(分子量50,000或以下)的方法。 |
| A:由于该试剂盒中包含的过滤管是分子量截断值为30K的超滤过滤器,因此我们建议使用50,000或分子量更大的蛋白质,并留有余量。
当标记分子量为50,000或更小的蛋白质时,可以通过更换为分子量分数较小的超滤过滤器来标记甚至很小的蛋白质,如下所示。 —————————————— PALL Nanocep 3K产品编号OD003C33 PALL Nanocep 10K产品编号OD010C33 —————————————— 离心所需的时间可能比试剂盒中随附的过滤器要长,因此请注意离心时间。 |
| Q5:标记后,离心过滤管,液体仍会留在膜上怎么处理? |
| A:(1)目视检查隔膜时,如果液体稍微残留在隔膜杯的边缘,请继续执行下面操作。如果倾斜和旋转膜杯时液体残留在膜上或滴下,请以8,000 g离心约15至30分钟。
(2)即使在1)中的离心操作之后,如果液体仍留在膜上,请检查标记物质是否聚集。根据抗体或蛋白质本身的特性,用小分子标记剂进行标记可能会增加抗体或蛋白质的疏水性并使其聚集。如果在标记的物质上观察到团聚,将其转移到另一个微管中一次,离心并使用上清液。 (回收的抗体/蛋白质的量将减少。) *如果您怀疑过滤器堵塞,可以通过更换新的膜过滤器来解决。 替代品:PALL Nanocep 30K(制造商代码:OD030C33) |
| Q6:该试剂盒可以标记什么? |
| A:可以标记分子量为“ 50,000或更高”和反应性氨基(NH2)的化合物(抗体,蛋白质等)。标记样品量为“50-200μg”。
*当考虑标记“ mg”的量时,也可以使用“生物素化试剂盒(Sulfo-OSu);同仁产品货号:BK01”。 *由于试剂盒附带的过滤管为30K,因此无法纯化低分子量化合物。 |
| Q7:一个IgG分子能标记多少生物素? |
| A:每个IgG分子平均能标记7至10个生物素。 |
| Q8:标记产物能保存多久? |
| A:在0-5℃下能够保存2个月。如果需要保存更久,可以添加等量的丙三醇,并在-20℃下 (只要该蛋白可以冷冻) 存放。但是,还要注意样品自身是否稳定。 |
| Q9:能不能用这个试剂盒标记寡核苷酸和寡肽? |
| A:不能,寡核苷酸和寡肽的分子量太小不能使其保留在过滤膜上。请参照Q4。 |
| Q10:含有生物素标记蛋白质的活细胞怎么处理? |
| A:我们推荐使用PBS (含2-10% FBS) 制备细胞悬液,保持最佳细胞状态。 |
| Q11:回收缓冲液 (WS Buffer)对活细胞有危害吗? |
| A:没有。WS Buffer含有表面活性剂,它的浓度控制在对细胞没有毒性的范围内。如果您担心WS Buffer中的添加剂,请您使用常用的缓冲液代替。 |
参考文献
1) Y. Kubota, Y. Oike, S. Satoh, Y. Tabata, Y. Niikura, T. Morisada, M. Akao, T. Urano, Y. Ito, T. Miyamoto, N. Nagai, G. Y. Koh, S. Watanabe and T. Suda, “Cooperative Interaction of Angiopoietin-like Proteins 1 and 2 in Zebrafish Vascular Development “, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2005, 102(38), 13502.
2) T. Yamabuki, A. Takano, S. Hayama, N. Ishikawa, T. Kato, M. Miyamoto, T. Ito, H. Ito, Y. Miyagi, H. Nakayama, M. Fujita, M. Hosokawa, E. Tsuchiya, N. Kohno, S. Kondo, Y. Nakamura and Y. Daigo, “Dikkopf-1 as a Novel Serologic and Prognostic Biomarker for Lung and Esophageal Carcinomas”, Cancer Res., 2007, 67, 2517.
3) H. Kohara, Y. Omatsu, T. Suhiyama, M. Noda, N. Fujii and T. Nagasawa, “Development of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Bone Marrow Stromal Cell niches Requires CXCL12-CXCR4 Chemokine Signaling”, Blood, 2007, 110(13), 4153.
4) N. Ishikawa, A. Takano, W. Yasui, K. Inai, H. Nishimura, H. Ito, Y. Miyagi, H. Nakayama, M. Fujita, M. Hosokawa, E. Tsuchiya, N. Kohno, Y. Nakamura and Y. Daigo, “Cancer-testis Antigen Lymphocyte Antigen 6 Complex Locus K is a Serologic Biomarker and a Therapeutic Target for Lung and Esophageal Carcinomas”, Cancer Res., 2007, 67(24), 11601.
5) A. Fukuda, T. Goto, K.N. Kuroishi, K.K. Gunjigake, S. Kataoka, S. Kobayashi and K. Yamaguchi, “Hemokinin-1 competitively inhibits substance P-induced stimulation of osteoclast formation and function”, Neuropeptides., 2013, 47, (4), 251.
6) A. Ogawa , M. Sakatsume, X. Wang, Y. Sakamaki, Y. Tsubata, B. Alchi, T. Kuroda, H. Kawachi, I. Narita, F. Shimizu and F. Gejyo, “SM22alpha: the novel phenotype marker of injured glomerular epithelial cells in anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis”, Nephron Exp. Nephrol.., 2007, 106, (3), e77.
7) D. Men, T.T. Zhang, L.W. Hou, J. Zhou, Z.P. Zhang, Y.Y. Shi, J.L. Zhang, Z.Q. Cui, J.Y. Deng, D.B. Wang and X.E. Zhang, “Self-Assembly of Ferritin Nanoparticles into an Enzyme Nanocomposite with Tunable Size for Ultrasensitive Immunoassay”, ACS Nano., 2015, 9, (11), 10852.
8) D. Sugahara, Y. Kobayashi, Y. Akimoto, H. Kawakami, “Mouse intestinal niche cells express a distinct α1,2-fucosylated glycan recognized by a lectin from Burkholderia cenocepacia”, Glycobiology., 2017, 27, (3), 246.
9) H. Sasaki-Iwaoka, M. Ohori, A. Imasato, K. Taguchi, K. Minoura, T. Saito, K. Kushima, E. Imamura, S. Kubo, S. Furukawa and T. Morokata, “Generation and characterization of a potent fully human monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-23 receptor”, Eur. J. Pharmacol.., 2018, 828, 89.
10) K. Kaneshiro, M. Watanabe, K. Terasawa, H. Uchimura, Y. Fukuyama, S. Iwamoto, T.A. Sato, K. Shimizu, G. Tsujimoto and K. Tanaka, “Rapid quantitative profiling of N-glycan by the glycan-labeling method using 3-aminoquinoline/α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid”, Anal. Chem.., 2012, 84, (16), 7146.
11) K.S. Tan, K. Kulkeaw, Y. Nakanishi, D. Sugiyama, “Expression of cytokine and extracellular matrix mRNAs in fetal hepatic stellate cells”, Genes Cells., 2017, 22, (9), 836.
12) M. Tahara, S. Ohno, K. Sakai, Y. Ito, H. Fukuhara, K. Komase, M.A. Brindley, P.A. Rota, R.K. Plemper, K. Maenaka and M. Takeda, “The receptor-binding site of the measles virus hemagglutinin protein itself constitutes a conserved neutralizing epitope”, J. Virol.., 2013, 87, (6), 3583.
13) M. Takahashi, Y. Ishida, D. Iwaki, K. Kanno, T. Suzuki, Y. Endo, Y. Homma and T. Fujita, “Essential role of Mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease-1 in activation of the complement factor D”, J. Exp. Med.., 2010, 207, (1), 29.
14) N. Hosen, Y. Matsunaga, K. Hasegawa, H. Matsuno, Y. Nakamura, M. Makita, K. Watanabe, M. Yoshida, K. Satoh, S. Morimoto, F. Fujiki, H. Nakajima, J. Nakata, S. Nishida, A. Tsuboi, Y. Oka, M. Manabe, H. Ichihara, Y. Aoyama, A. Mugitani , T. Nakao, M. Hino, R. Uchibori, K. Ozawa, Y. Baba, S. Terakura, N. Wada, E. Morii, J. Nishimura, K. Takeda, Y. Oji, H. Sugiyama, J. Takagi and A. Kumanogoh, “The activated conformation of integrin β7 is a novel multiple myeloma-specific target for CAR T cell therapy”, Nat. Med.., 2017, 23, (12), 1436.
15) R. Nishino, A. Takano, H. Oshita, N. Ishikawa, H. Akiyama, H. Ito, H. Nakayama, Y. Miyagi, E. Tsuchiya, N. Kohno, Y. Nakamura and Y. Daigo, “Identification of Epstein-Barr virus–induced gene 3 as a novel serum and tissue biomarker and a therapeutic target for lung cancer”, Clin. Cancer Res.., 2011, 17, (19), 6272.
16) T. Hiono, A. Matsuda, T. Wagatsuma, M. Okamatsu, Y. Sakoda and A. Kuno, “Lectin microarray analyses reveal host cell-specific glycan profiles of the hemagglutinins of influenza A viruses”, Virology., 2019, 527, 132.
17) T. Oshima, S. Sato, J. Kato, Y. Ito, T. Watanabe, I. Tsuji, A. Hori, T. Kurokawa and T. Kokubo, “Nectin-2 is a potential target for antibody therapy of breast and ovarian cancers”, Mol. Cancer., 2013, 12, (60), .
18) T. Yoshida, N. Shiraki, H. Baba, M. Goto, S. Fujiwara, K. Kume and S. Kume, “Expression patterns of epiplakin1 in pancreas, pancreatic cancer and regenerating pancreas”, Genes Cells., 2008, 13, (7), 667.
19) X. Piao, T. Ozawa, H. Hamana, K. Shitaoka, A. Jin, H. Kishi and A. Muraguchi, “TRAIL-receptor 1 IgM antibodies strongly induce apoptosis in human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo”, Oncoimmunology., 2016, 5, (5), e1131380.
20) Y. Shimazaki, Y. Kohno, “Successive analysis of antigen trapping and enzymatic digestion on membrane-immobilized avidin”, Anal. Biochem.., 2012, 422, (1), 55.
关联产品
实验工具|稀释计算器|摩尔浓度计算器
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
品名货号用途
| Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK03 | 生物素标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2 (for 1mg)试剂盒 | LK55 | 生物素标记-氨基(1 mg/sample) |
| Biotin Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK10 | 生物素标记-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid Biotin Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK37 | 生物素标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| Biotinylation Kit (Sulfo-OSu)试剂 | BK01 | 生物素标记-氨基(1-5 mg/sample) |
| Biotin-PE-maleimide试剂 | B592 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-SS-Sulfo-Osu试剂 | B572 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-AC5-Osu试剂 | B305 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-(AC5)2-Osu试剂 | B306 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-Osu试剂 | B304 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-PEAC5-maleimide试剂 | B299 | 生物素 |
| ARP(Aldehyde Reactive Probe)试剂 | A305 | 生物素 |
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理日本同仁化学 DOJINDO代理商全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多信息
蛋白抗体标记
品名货号用途
| Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK03 | 生物素标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2 (for 1mg)试剂盒 | LK55 | 生物素标记-氨基(1 mg/sample) |
| Biotin Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK10 | 生物素标记-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid Biotin Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK37 | 生物素标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| Biotinylation Kit (Sulfo-OSu)试剂 | BK01 | 生物素标记-氨基(1-5 mg/sample) |
| Biotin-PE-maleimide试剂 | B592 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-SS-Sulfo-Osu试剂 | B572 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-AC5-Osu试剂 | B305 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-(AC5)2-Osu试剂 | B306 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-Osu试剂 | B304 | 生物素 |
| Biotin-PEAC5-maleimide试剂 | B299 | 生物素 |
| ARP(Aldehyde Reactive Probe)试剂 | A305 | 生物素 |
| CLAMP F405-Signal Boosting | C554 | 检测细胞表面抗原(免疫荧光法) |
| Fluorescein Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK01 | FITC(488激发)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| HiLyte Fluor 555 Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK14 | 荧光素(555激发)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| HiLyte Fluor 647 Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK15 | 荧光素(647激发)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid Fluorescein Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK32 | FITC(488激发)标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid HiLyte Fluor 555 Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK35 | 荧光素(555激发)标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid HiLyte Fluor 647 Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK36 | 荧光素(647激发)标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| FITC-I试剂 | F007 | 荧光素FITC |
| Peroxidase Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK11 | 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Peroxidase Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK09 | 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Peroxidase Labeling Kit – NH2 (for 1mg)试剂盒 | LK51 | 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记-氨基(1 mg/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid Peroxidase Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK33 | 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| Alkaline Phosphatase Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK12 | 碱性磷酸酶标记(ALP)-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Alkaline Phosphatase Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK13 | 碱性磷酸酶标记(ALP)-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Isothiocyanobenzyl-EDTA试剂 | M030 | 螯合标记 |
| Isothiocyanobenzyl-NTA试剂 | I279 | 蛋白抗体标记 |
| FeBABE试剂 | F279 | 蛋白抗体标记 |
| AB-NTA free acid试剂 | A459 | 螯合标记 |
| Maleimido-C3-NTA试剂 | M035 | N-[5-(3′-马来酰亚胺丙烷基氨基)-1-戊基羧基]亚氨基二乙酸, 二钠盐, 一水合物 |
| DTPA anhydride试剂 | D033 | 螯合标记 |
| Allophycocyanin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK21 | 藻蓝蛋白(APC)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Allophycocyanin Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK24 | 藻蓝蛋白(APC)标记-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK23 | 藻红蛋白(PE)标记-氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 | LK26 | 藻红蛋白(PE)标记-巯基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Ab-10 Rapid R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit试剂盒 | LK34 | R-藻红蛋白(PE)抗体标记-氨基(10 ug/sample) |
| ICG Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | LK31 | ICG 标记氨基(50-200ug/sample) |
| Sulfo-AC5-SPDP试剂 | S359 | IgG纯化分离 |
| DTSSP试剂 | D630 | 交联剂 |
| BS3试剂 | B574 | 交联剂 |
| DSP试剂 | D629 | 交联剂 |
| EMCS试剂 | E018 | 交联剂 |
| GMBS试剂 | G005 | 交联剂 |
| SPDP试剂 | S291 | 交联剂 |
| Sulfo-SMCC试剂 | S330 | 交联剂 |
抗体标记试剂盒可满足各种实验需求
1、我想对蛋白质进行定量
| ELISA法
|
FCM
|
蛋白质印迹
|
2、我想看看蛋白质在哪里表达
影像学观察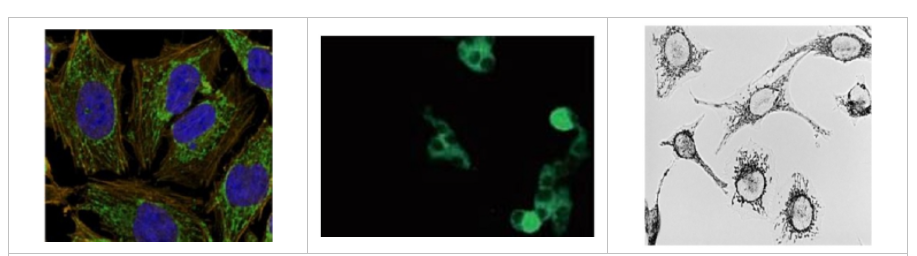
3、该试剂盒可以很容易地进行蛋白质标记
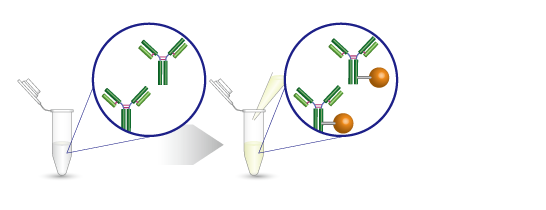
4、客户对抗体标记试剂盒的反馈

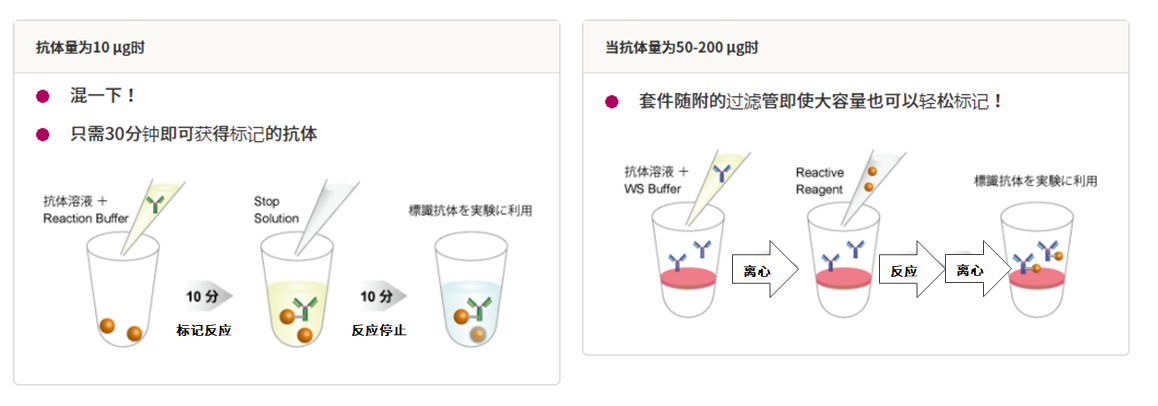
5、操作方法非常简单
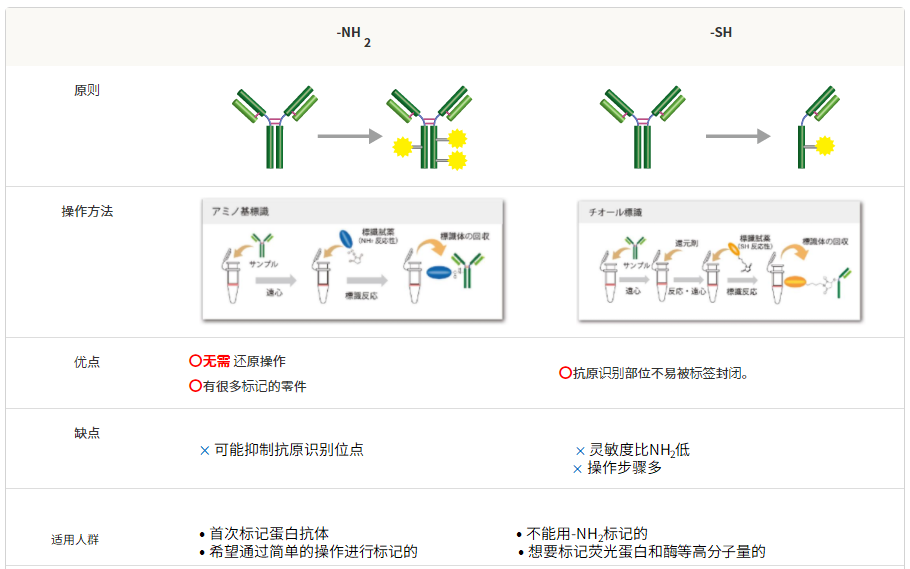
6、可与-NH2和-SH标记方法兼容
生物素标记试剂盒

生物素标记试剂盒原理
适用人群

影像实验例
使用的试剂盒:Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒
FCM实验示例
使用的试剂盒:Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒
竞争抑制
用生物素标记试剂盒-NH2对抗X抗体进行生物素标记,然后使用链霉亲和素-APC通过流式细胞术进行分析。
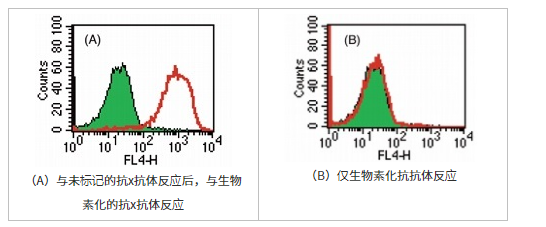
抗原未标记的抗×抗体被抗体(A)封闭时,未观察到由于抗体的竞争性抑制而引起的生物素化抗x抗体的反应,仅反应了生物素化抗x抗体(B)的阳性部分。即使使用自制的标记抗体,也可以以很少的非特异性反应进行充分的检测反应。
(数据由北海道大学遗传医学研究所大仓黑木章博士,今茂茂重博士提供)
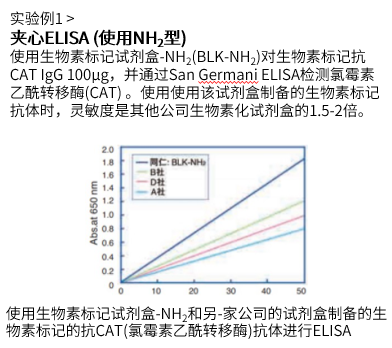
ELISA实验实例
| 使用的试剂盒:Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒 | 使用的试剂盒:Biotin Labeling Kit – SH试剂盒 |
 |
 |
产品列表
| 生物素 | 样品数量/类型 | 标记对象 | 产品名称 | 分析方法 |
| 生物素 | 10μg抗体 | -NH2 | Ab-10 Rapid Biotin Labeling Kit |  |
| 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | Biotin Labeling Kit -NH2 | ||
| -SH | Biotin Labeling Kit -SH | |||
| 1mg抗体 | -NH2 | Biotin Labeling Kit – NH2 (for 1mg) | ||
| 1-5 mg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | Biotinylation Kit (Sulfo-OSu) |
荧光染料/荧光蛋白标记试剂盒
生物素标记试剂盒原理
适用人群

使用的试剂盒:Ab-10 Rapid Fluorescein Labeling Kit, Ab-10 Rapid HiLyte Fluor™ 555 Labeling Kit
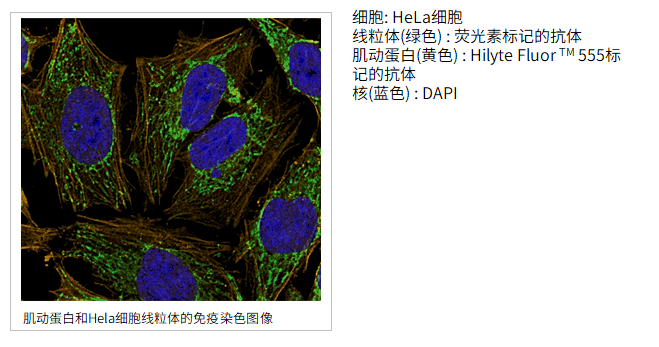
使用的试剂盒:ICG Labeling Kit – NH2试剂盒
竞争抑制
用生物素标记试剂盒-NH2对抗X抗体进行生物素标记,然后使用链霉亲和素-APC通过流式细胞仪进行分析。

FCM实验示例
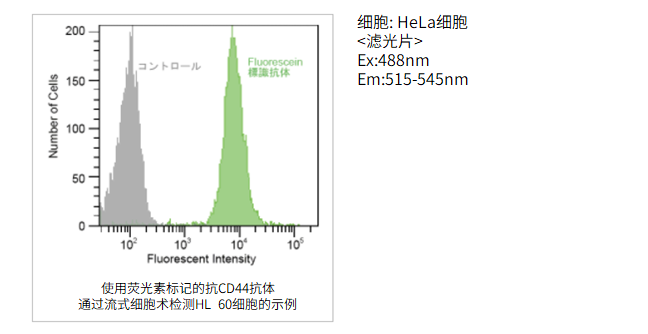
使用的试剂盒:Ab-10 Rapid Fluorescein Labeling Kit
使用Ab-10快速荧光素标记试剂盒用抗CD44抗体(10μg)标记后,对HL60细胞进行免疫染色。
产品列表
| 荧光染料 | 样品数量/类型 | 标记对象 | 产品名称 | 分析方法 |
| 荧光素 | 10μg抗体 | -NH2 | Ab-10 Rapid Fluorescein Labeling Kit |  |
| 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | Fluorescein Labeling Kit -NH2 | ||
| HiLyte Fluor™ | 10μg抗体 | -NH2 | Ab-10 Rapid HiLyte Fluor™ 555 / 647 Labeling Kit -NH2 | |
| 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | HiLyte Fluor™ 555 / 647 Labeling Kit -NH2 |
||
| ICG | 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | ICG Labeling Kit-NH2 |
| 荧光蛋白 | 样品数量/类型 | 标记对象 | 产品名称 | 分析方法 |
| R-藻红蛋白 | 10μg抗体 | -NH2 | Ab-10 Rapid R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit |  |
| 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit-NH2 | ||
| -SH | R-Phycoerythrin Labeling Kit-SH | |||
| 异花青素 | 50-200μg抗体/蛋白质 | -NH2 | Allophycocyanin Labeling Kit-NH2 | |
| -SH | Allophycocyanin Labeling Kit-SH |
酶标试剂盒
适用人群

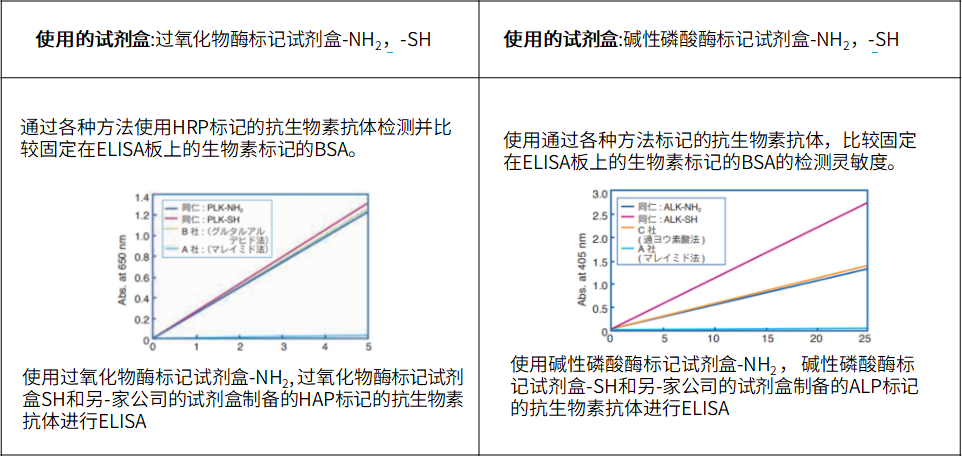
ELISA实验实例
蛋白质印迹实验例

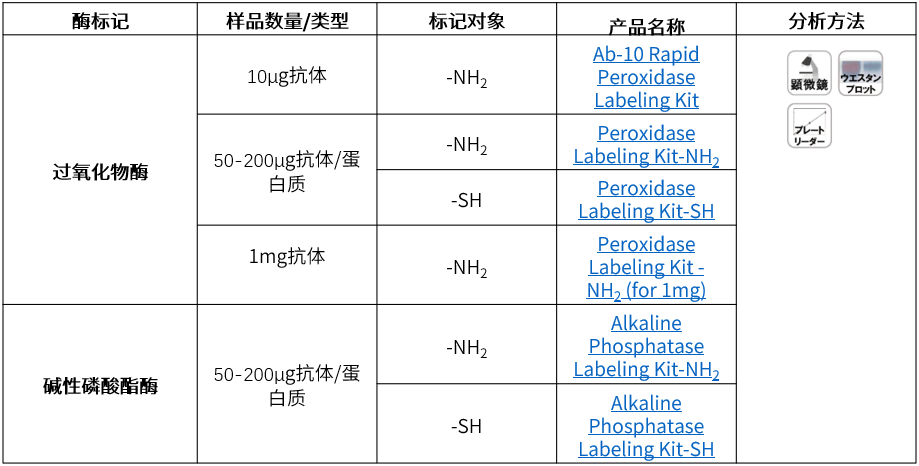
产品列表
VECTOR SBA生物素标记的大豆凝集素
VECTOR SBA生物素标记的大豆凝集素
|
isolated from Glycine max (soybean) seeds |
| Composed of four subunits of approximay equal size, soybean agglutinin is a family of closely related isolectins. This glycoprotein has a molecular weight of about 120,000 and an isoelectric point near pH 6.0. SBA preferentially binds to oligosaccharide structures with terminal a- or b-linked N-acetylgalactosamine, and to a lesser extent, galactose residues. Binding can be blocked by substitutions on penultimate sugars, such as fucose attached to the penultimate galactose in blood group B substance. SBA has been used in glycoprotein fractionation, histochemical applications and cell sorter analysis. |
|
An important application for SBA is the separation of pluripotential stem cells from human bone marrow. Cells fractionated by SBA do not produce graft vs host disease and can be used in bone marrow transplantation across histocompatibility barriers (references available upon request). It should be noted that some forms of SBA seem to be excellent in separating human cells while others are better for cells of other species. VECTOR SBA生物素标记的大豆凝集素 This biotinylated lectin conjugate is prepared from affinity-purified lectin and is optimally labeled with biotin. Essentially free of inactive lectin conjugate and containing no free biotin, this biotinylated lectin provides an ideal intermediate for examining glycoconjugates using the Biotin-Avidin System. First the biotin-labeled lectin is added, followed by the VECTASTAIN® ABC Reagent, Avidin D conjugate, or streptavidin derivative. Another possible application is in the isolation of lymphokines and other products of mitogenic stimulation. |
| Inhibiting/Eluting Sugar: 200 mM N-acetylgalactosamine |
VECTOR生物素Jacalin Biotinylated Jacalin
VECTOR生物素Jacalin Biotinylated Jacalin
isolated from Artocarpus integrifolia (Jackfruit) seeds
Jacalin is a lectin composed of four subunits, two of approximay 10,000 daltons and two of 16,000 daltons each. This 50,000 dalton glycoprotein appears to bind only O-glycosidically linked oligosaccharides, preferring the structure galactosyl (b-1,3) N-acetylgalactosamine. This structure (the so-called “T-antigen”) is the oligosaccharide to which peanut agglutinin binds. However, unlike PNA, Jacalin will bind this structure even in a mono- or disialylated form. This lectin has been used to purify human IgA, since no other human immunoglobulin class binds Jacalin (references available upon request). The specificity of this lectin also affords the opportunity to localize or isolate glycoproteins with O-glycosidically linked oligosaccharide side chains.
This biotinylated lectin conjugate is prepared from affinity-purified lectin and is optimally labeled with biotin. Essentially free of inactive lectin conjugate and containing no free biotin, this biotinylated lectin provides an ideal intermediate for examining glycoconjugates using the Biotin-Avidin System. First the biotin-labeled lectin is added, followed by the VECTASTAIN® ABC Reagent, Avidin D conjugate, or streptavidin derivative. Another possible application is in the isolation of lymphokines and other products of mitogenic stimulation.
Inhibiting/Eluting Sugar: 800 mM galactose or 100 mM melibiose
VECTOR生物素Jacalin Biotinylated Jacalin 详细产品信息可和选购
VECTOR GNL生物素雪花莲凝集素Biotinylated Galanthus Nivalis
VECTOR GNL生物素雪花莲凝集素Biotinylated Galanthus Nivalis Lectin
The following protocols offer guidelines for assay development using lectin-based detection of glycoproteins
present in tissue sections, adsorbed onto microtiter plates, or transferred from electrophoretic
gels onto nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes.
Histochemistry:
1a. Staining procedure for paraffin sections: Deparaffinize and hydrate tissue sections through
xylenes or other clearing agents and graded alcohol series and rinse for 5 minutes in tap water.
If required, retrieve antigens using the Antigen Unmasking Solution (H-3300 or H-3301).
1b. Staining procedure for frozen sections: Air dry sections. Immediay before staining, fix
sections with acetone. Transfer slices to buffer. If endogenous enzyme activities are present,
inactivate using appropriate methods.
2. Perform Streptavidin/Biotin blocking if required following kit instructions (SP-2002). Do not
use SP-2001. Block non-specific binding by incubating section with Carbo-Free™ Blocking
Solution (Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Blot excess blocking solution
from the sections.
3. Apply biotinylated lectin at approximay 2-20 μg/ml in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, 150
mM NaCl, pH 7.4) to the sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with
TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase,
ImmPACT™ DAB (Cat. No. SK-4105) is recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Vector® Red
(Cat. No. SK-5100). Rinse in tap water.
6. Counterstain (optional), clear and mount. For galactose or GalNAc-specific lectins avoid mounting
in glycerol-based mounting media.
ELISA:
1. Adsorb target protein to microtiter plate by placing 50-200 μl of approximay 3 μg/ml glycoprotein
solution into the desired wells. Some wells may be left untreated as negative controls. Incubate at
37 ºC for 1 hour. Wash wells three times with TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
2. Block non-specific binding by filling each well to the brim with Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution
(Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
3. Apply 50-200 μl of approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin in PBS to the wells and incubate
for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
wells and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate non-precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For
peroxidase, ABTS (Cat. No. SK-4500) is recommended; for alkaline phophatase, pNPP (Cat. No.
SK-5900).
6. Quantify the colored reaction product by spectrophotometry.
Western Blot:
1. Perform electrophoresis and transfer proteins to a membrane according to standard procedures.
2. Block non-specific binding by incubating the membrane in Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution (Cat.
No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Use a sufficient volume to compley cover
the membrane.
3. Incubate membrane in PBS containing approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin for 30 minutes
at room temperature. Wash with TPBS (PBS +0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Incubate the
membrane in the reagent for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase, DuoLuX™
Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Substrate for Peroxidase (Cat. No. SK-6604) or ImmPACT™ DAB
(Cat. No. SK-4105) are recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent
Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase (Cat. No. SK-6605) or BCIP/NBT (Cat. No. SK-5400) are
recommended.
Negative Controls
Negative controls should be run in parallel in each of the above described methodologies to validate
binding results. When applying lectins, one of the most appropriate negative controls is to preabsorb
the lectin with a concentration of a defined sugar, with which, the lectin has a known high affinity.
Vector Labs offers a series of sugars that are intended for such a purpose.
The lectin is diluted to a suitable working concentration in a solution containing approximay
200 mM to 500 mM of the sugar. This mixture is left to bind at room temperature for 30 to 60 min.
Following this absorption incubation, the mixture is substituted into the procedure in place of the unabsorbed
lectin and incubated under the same conditions. The subsequent detection procedure is followed
as for the test method. In most cases the vast majority of lectin binding to the tissue section (membrane
blot, etc.) will be eliminated. Some trace binding to the section (blot etc) may still be present under
these conditions and probably indicates presence of secondary or tertiary sugar preferences. These negative
control results should be compared with the test results to determine specificity of binding
VECTOR EEL生物素大叶黄杨Europaeus凝集素
VECTOR EEL生物素大叶黄杨Europaeus凝集素
The following protocols offer guidelines for assay development using lectin-based detection of glycoproteins
present in tissue sections, adsorbed onto microtiter plates, or transferred from electrophoretic
gels onto nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes.
Histochemistry:
1a. Staining procedure for paraffin sections: Deparaffinize and hydrate tissue sections through
xylenes or other clearing agents and graded alcohol series and rinse for 5 minutes in tap water.
If required, retrieve antigens using the Antigen Unmasking Solution (H-3300 or H-3301).
1b. Staining procedure for frozen sections: Air dry sections. Immediay before staining, fix
sections with acetone. Transfer slices to buffer. If endogenous enzyme activities are present,
inactivate using appropriate methods.
2. Perform Streptavidin/Biotin blocking if required following kit instructions (SP-2002). Do not
use SP-2001. Block non-specific binding by incubating section with Carbo-Free™ Blocking
Solution (Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Blot excess blocking solution
from the sections.
3. Apply biotinylated lectin at approximay 2-20 μg/ml in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, 150
mM NaCl, pH 7.4) to the sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with
TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase,
ImmPACT™ DAB (Cat. No. SK-4105) is recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Vector® Red
(Cat. No. SK-5100). Rinse in tap water.
6. Counterstain (optional), clear and mount. For galactose or GalNAc-specific lectins avoid mounting
in glycerol-based mounting media.
ELISA:
1. Adsorb target protein to microtiter plate by placing 50-200 μl of approximay 3 μg/ml glycoprotein
solution into the desired wells. Some wells may be left untreated as negative controls. Incubate at
37 ºC for 1 hour. Wash wells three times with TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
2. Block non-specific binding by filling each well to the brim with Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution
(Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
3. Apply 50-200 μl of approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin in PBS to the wells and incubate
for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
wells and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate non-precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For
peroxidase, ABTS (Cat. No. SK-4500) is recommended; for alkaline phophatase, pNPP (Cat. No.
SK-5900).
6. Quantify the colored reaction product by spectrophotometry.
Western Blot:
1. Perform electrophoresis and transfer proteins to a membrane according to standard procedures.
2. Block non-specific binding by incubating the membrane in Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution (Cat.
No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Use a sufficient volume to compley cover
the membrane.
3. Incubate membrane in PBS containing approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin for 30 minutes
at room temperature. Wash with TPBS (PBS +0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Incubate the
membrane in the reagent for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase, DuoLuX™
Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Substrate for Peroxidase (Cat. No. SK-6604) or ImmPACT™ DAB
(Cat. No. SK-4105) are recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent
Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase (Cat. No. SK-6605) or BCIP/NBT (Cat. No. SK-5400) are
recommended.
VECTOR EEL生物素大叶黄杨Europaeus凝集素
Negative Controls
Negative controls should be run in parallel in each of the above described methodologies to validate
binding results. When applying lectins, one of the most appropriate negative controls is to preabsorb
the lectin with a concentration of a defined sugar, with which, the lectin has a known high affinity.
Vector Labs offers a series of sugars that are intended for such a purpose.
The lectin is diluted to a suitable working concentration in a solution containing approximay
200 mM to 500 mM of the sugar. This mixture is left to bind at room temperature for 30 to 60 min.
Following this absorption incubation, the mixture is substituted into the procedure in place of the unabsorbed
lectin and incubated under the same conditions. The subsequent detection procedure is followed
as for the test method. In most cases the vast majority of lectin binding to the tissue section (membrane
blot, etc.) will be eliminated. Some trace binding to the section (blot etc) may still be present under
these conditions and probably indicates presence of secondary or tertiary sugar preferences. These negative
control results should be compared with the test results to determine specificity of binding
详细产品信息可和选购
VECTOR 生物素曼陀罗凝集素Biotinylated Datura Stramonium Lec
VECTOR 生物素曼陀罗凝集素Biotinylated Datura Stramonium Lectin
The following protocols offer guidelines for assay development using lectin-based detection of glycoproteins
present in tissue sections, adsorbed onto microtiter plates, or transferred from electrophoretic
gels onto nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes.
Histochemistry:
1a. Staining procedure for paraffin sections: Deparaffinize and hydrate tissue sections through
xylenes or other clearing agents and graded alcohol series and rinse for 5 minutes in tap water.
If required, retrieve antigens using the Antigen Unmasking Solution (H-3300 or H-3301).
1b. Staining procedure for frozen sections: Air dry sections. Immediay before staining, fix
sections with acetone. Transfer slices to buffer. If endogenous enzyme activities are present,
inactivate using appropriate methods.
2. Perform Streptavidin/Biotin blocking if required following kit instructions (SP-2002). Do not
use SP-2001. Block non-specific binding by incubating section with Carbo-Free™ Blocking
Solution (Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Blot excess blocking solution
from the sections.
3. Apply biotinylated lectin at approximay 2-20 μg/ml in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, 150
mM NaCl, pH 7.4) to the sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with
TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase,
ImmPACT™ DAB (Cat. No. SK-4105) is recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Vector® Red
(Cat. No. SK-5100). Rinse in tap water.
6. Counterstain (optional), clear and mount. For galactose or GalNAc-specific lectins avoid mounting
VECTOR 生物素曼陀罗凝集素Biotinylated Datura Stramonium Lectin
in glycerol-based mounting media.
ELISA:
1. Adsorb target protein to microtiter plate by placing 50-200 μl of approximay 3 μg/ml glycoprotein
solution into the desired wells. Some wells may be left untreated as negative controls. Incubate at
37 ºC for 1 hour. Wash wells three times with TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
2. Block non-specific binding by filling each well to the brim with Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution
(Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
3. Apply 50-200 μl of approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin in PBS to the wells and incubate
for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
wells and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate non-precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For
peroxidase, ABTS (Cat. No. SK-4500) is recommended; for alkaline phophatase, pNPP (Cat. No.
SK-5900).
6. Quantify the colored reaction product by spectrophotometry.
Western Blot:
1. Perform electrophoresis and transfer proteins to a membrane according to standard procedures.
2. Block non-specific binding by incubating the membrane in Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution (Cat.
No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Use a sufficient volume to compley cover
the membrane.
3. Incubate membrane in PBS containing approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin for 30 minutes
at room temperature. Wash with TPBS (PBS +0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Incubate the
membrane in the reagent for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase, DuoLuX™
Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Substrate for Peroxidase (Cat. No. SK-6604) or ImmPACT™ DAB
(Cat. No. SK-4105) are recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent
Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase (Cat. No. SK-6605) or BCIP/NBT (Cat. No. SK-5400) are
recommended.
Negative Controls
Negative controls should be run in parallel in each of the above described methodologies to validate
binding results. When applying lectins, one of the most appropriate negative controls is to preabsorb
the lectin with a concentration of a defined sugar, with which, the lectin has a known high affinity.
Vector Labs offers a series of sugars that are intended for such a purpose.
The lectin is diluted to a suitable working concentration in a solution containing approximay
200 mM to 500 mM of the sugar. This mixture is left to bind at room temperature for 30 to 60 min.
Following this absorption incubation, the mixture is substituted into the procedure in place of the unabsorbed
lectin and incubated under the same conditions. The subsequent detection procedure is followed
as for the test method. In most cases the vast majority of lectin binding to the tissue section (membrane
blot, etc.) will be eliminated. Some trace binding to the section (blot etc) may still be present under
these conditions and probably indicates presence of secondary or tertiary sugar preferences. These negative
control results should be compared with the test results to determine specificity of binding
VECTOR BPL生物素菊紫荆凝集素Biotinylated Bauhinia Purpurea
VECTOR BPL生物素菊紫荆凝集素Biotinylated Bauhinia Purpurea Lectin
The following protocols offer guidelines for assay development using lectin-based detection of glycoproteins
present in tissue sections, adsorbed onto microtiter plates, or transferred from electrophoretic
gels onto nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes.
Histochemistry:
1a. Staining procedure for paraffin sections: Deparaffinize and hydrate tissue sections through
xylenes or other clearing agents and graded alcohol series and rinse for 5 minutes in tap water.
If required, retrieve antigens using the Antigen Unmasking Solution (H-3300 or H-3301).
1b. Staining procedure for frozen sections: Air dry sections. Immediay before staining, fix
sections with acetone. Transfer slices to buffer. If endogenous enzyme activities are present,
inactivate using appropriate methods.
2. Perform Streptavidin/Biotin blocking if required following kit instructions (SP-2002). Do not
use SP-2001. Block non-specific binding by incubating section with Carbo-Free™ Blocking
Solution (Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Blot excess blocking solution
from the sections.
3. Apply biotinylated lectin at approximay 2-20 μg/ml in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, 150
mM NaCl, pH 7.4) to the sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with
TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase,
ImmPACT™ DAB (Cat. No. SK-4105) is recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Vector® Red
(Cat. No. SK-5100). Rinse in tap water.
6. Counterstain (optional), clear and mount. For galactose or GalNAc-specific lectins avoid mounting
in glycerol-based mounting media.
ELISA:
1. Adsorb target protein to microtiter plate by placing 50-200 μl of approximay 3 μg/ml glycoprotein
solution into the desired wells. Some wells may be left untreated as negative controls. Incubate at
37 ºC for 1 hour. Wash wells three times with TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
2. Block non-specific binding by filling each well to the brim with Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution
(Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
3. Apply 50-200 μl of approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin in PBS to the wells and incubate
for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
wells and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate non-precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For
peroxidase, ABTS (Cat. No. SK-4500) is recommended; for alkaline phophatase, pNPP (Cat. No.
SK-5900).
6. Quantify the colored reaction product by spectrophotometry.
Western Blot:
1. Perform electrophoresis and transfer proteins to a membrane according to standard procedures.
2. Block non-specific binding by incubating the membrane in Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution (Cat.
No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Use a sufficient volume to compley cover
the membrane.
3. Incubate membrane in PBS containing approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin for 30 minutes
at room temperature. Wash with TPBS (PBS +0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Incubate the
membrane in the reagent for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase, DuoLuX™
Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Substrate for Peroxidase (Cat. No. SK-6604) or ImmPACT™ DAB
(Cat. No. SK-4105) are recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent
Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase (Cat. No. SK-6605) or BCIP/NBT (Cat. No. SK-5400) are
recommended.
Negative Controls
Negative controls should be run in parallel in each of the above described methodologies to validate
binding results. When applying lectins, one of the most appropriate negative controls is to preabsorb
the lectin with a concentration of a defined sugar, with which, the lectin has a known high affinity.
Vector Labs offers a series of sugars that are intended for such a purpose.
The lectin is diluted to a suitable working concentration in a solution containing approximay
200 mM to 500 mM of the sugar. This mixture is left to bind at room temperature for 30 to 60 min.
Following this absorption incubation, the mixture is substituted into the procedure in place of the unabsorbed
lectin and incubated under the same conditions. The subsequent detection procedure is followed
as for the test method. In most cases the vast majority of lectin binding to the tissue section (membrane
blot, etc.) will be eliminated. Some trace binding to the section (blot etc) may still be present under
these conditions and probably indicates presence of secondary or tertiary sugar preferences. These negative
control results should be compared with the test results to determine specificity of binding
VECTOR 生物素苋尾状凝集素(ACL,ACA) BIOTIN-ACL
VECTOR 生物素苋尾状凝集素(ACL,ACA) BIOTIN-ACL
The following protocols offer guidelines for assay development using lectin-based detection of glycoproteins
present in tissue sections, adsorbed onto microtiter plates, or transferred from electrophoretic
gels onto nitrocellulose or PVDF membranes.
Histochemistry:
1a. Staining procedure for paraffin sections: Deparaffinize and hydrate tissue sections through
xylenes or other clearing agents and graded alcohol series and rinse for 5 minutes in tap water.
If required, retrieve antigens using the Antigen Unmasking Solution (H-3300 or H-3301).
1b. Staining procedure for frozen sections: Air dry sections. Immediay before staining, fix
sections with acetone. Transfer slices to buffer. If endogenous enzyme activities are present,
inactivate using appropriate methods.
2. Perform Streptavidin/Biotin blocking if required following kit instructions (SP-2002). Do not
use SP-2001. Block non-specific binding by incubating section with Carbo-Free™ Blocking
Solution (Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Blot excess blocking solution
from the sections.
3. Apply biotinylated lectin at approximay 2-20 μg/ml in PBS (10 mM sodium phosphate, 150
mM NaCl, pH 7.4) to the sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with
TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
sections and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase,
ImmPACT™ DAB (Cat. No. SK-4105) is recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Vector® Red
(Cat. No. SK-5100). Rinse in tap water.
6. Counterstain (optional), clear and mount. For galactose or GalNAc-specific lectins avoid mounting
in glycerol-based mounting media.
VECTOR 生物素苋尾状凝集素(ACL,ACA) BIOTIN-ACL
ELISA:
1. Adsorb target protein to microtiter plate by placing 50-200 μl of approximay 3 μg/ml glycoprotein
solution into the desired wells. Some wells may be left untreated as negative controls. Incubate at
37 ºC for 1 hour. Wash wells three times with TPBS (PBS + 0.05% Tween™20).
2. Block non-specific binding by filling each well to the brim with Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution
(Cat. No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
3. Apply 50-200 μl of approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin in PBS to the wells and incubate
for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Apply to the
wells and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash wells three times with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate non-precipitating substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For
peroxidase, ABTS (Cat. No. SK-4500) is recommended; for alkaline phophatase, pNPP (Cat. No.
SK-5900).
6. Quantify the colored reaction product by spectrophotometry.
Western Blot:
1. Perform electrophoresis and transfer proteins to a membrane according to standard procedures.
2. Block non-specific binding by incubating the membrane in Carbo-Free™ Blocking Solution (Cat.
No. SP-5040) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Use a sufficient volume to compley cover
the membrane.
3. Incubate membrane in PBS containing approximay 2-20 μg/ml biotinylated lectin for 30 minutes
at room temperature. Wash with TPBS (PBS +0.05% Tween™20).
4. Prepare VECTASTAIN®
® ABC (peroxidase, Cat. No. PK-6100) or VECTASTAIN® ABC-AP
(alkaline phosphatase, Cat. No. AK-5000) reagents according to the kit instructions. Incubate the
membrane in the reagent for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash with TPBS.
5. Apply an appropriate substrate for the enzyme system used in step 4. For peroxidase, DuoLuX™
Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent Substrate for Peroxidase (Cat. No. SK-6604) or ImmPACT™ DAB
(Cat. No. SK-4105) are recommended; for alkaline phosphatase, Chemiluminescent/Fluorescent
Substrate for Alkaline Phosphatase (Cat. No. SK-6605) or BCIP/NBT (Cat. No. SK-5400) are
recommended.
Negative Controls
Negative controls should be run in parallel in each of the above described methodologies to validate
binding results. When applying lectins, one of the most appropriate negative controls is to preabsorb
the lectin with a concentration of a defined sugar, with which, the lectin has a known high affinity.
Vector Labs offers a series of sugars that are intended for such a purpose.
The lectin is diluted to a suitable working concentration in a solution containing approximay
200 mM to 500 mM of the sugar. This mixture is left to bind at room temperature for 30 to 60 min.
Following this absorption incubation, the mixture is substituted into the procedure in place of the unabsorbed
lectin and incubated under the same conditions. The subsequent detection procedure is followed
as for the test method. In most cases the vast majority of lectin binding to the tissue section (membrane
blot, etc.) will be eliminated. Some trace binding to the section (blot etc) may still be present under
these conditions and probably indicates presence of secondary or tertiary sugar preferences. These negative
control results should be compared with the test results to determine specificity of binding
上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理New England Biolabs(NEB)酶试剂全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多产品信息和订购。
3´ –脱硫生物素标记 GTP 中无 RNase 和切刻酶污染。
有关该产品特性和应用的相关文献请登陆 www.neb-china.com 或 www.neb.com。