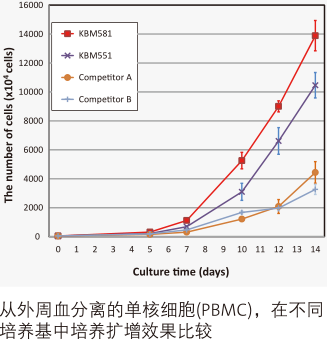
参考文献
A comparison of strategies for immortalizing mouse embryonic fibroblasts: M.M. St. Amad, et al.; J. Biol. Methods 3, e41 (2016), Application(s): Detected autophagy induction in SV40 transformed versus serially passed MEFs, 全文
Astemizole-Histamine induces Beclin-1-independent autophagy by targeting p53-dependent crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: R. Jakhar, et al.; Cancer Lett. 372, 89 (2016), Application(s): Flow cytometry analysis, 摘要;
Atg5 Is Essential for the Development and Survival of Innate Lymphocytes: T.E. O'Sullivan, et al.; Cell Rep. 15, 1910 (2016), Application(s): Liver lymphocytes were harvested and stained with cell surface antibodies and then incubated with 1:400 Cyto-ID Autophagy Detection Reagent, 摘要; 全文
Autophagy-related gene 5 and Wnt5 signaling pathway requires differentiation of embryonic stem cells into odontoblast-like cells: N. Ozeki, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 341, 92 (2016), Application(s): Autophagy flux, 摘要;
DHA-induced stress response in human colon cancer cells-focus on oxidative stress and autophagy: K. Pettersen, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 90, 158 (2016), Application(s):Autophagy determined by flow cytometry, 摘要;
Diosgenin induces ROS-dependent autophagy and cytotoxicity via mTOR signaling pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cells: S. Jiang, et al.; Phytomedicine 23, 243 (2016),Application(s): Confocal immunofluorescence, 摘要;
Efavirenz causes oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy in endothelial cells: M. Weiss, et al.; Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 16, 90 (2016), 摘要;
MiR-193b promotes autophagy and non-apoptotic cell death in oesophageal cancer cells: M.J. Nyhan, et al.; BMC Cancer 16, 101 (2016), Application(s): Assay used to stain live cells, 摘要; 全文
(Pro)renin receptor regulates autophagy and apoptosis in podocytes exposed to high glucose: C. Li, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 309, E302 (2015), Application(s):Confocal microscopy using mouse podocytes, 摘要;
A rapid and high content assay that measures cyto-ID-stained autophagic compartments and estimates autophagy flux with potential clinical applications: S. Guo, et al.; Autophagy11, 560 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescent detection, Microplate Reader , 摘要; 全文
A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal Erythropoiesis: R. Liang, et al.; PLoS Genet. 11, e1005526 (2015), Application(s):Autophagy flux measured by flow cytometry , 摘要; 全文
ABT-888 enhances cytotoxic effects of temozolomide independent of MGMT status in serum free cultured glioma cells: R.K. Balvers, et al.; J. Transl. Med. 13, 74 (2015),Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
Activation of autophagy in response to nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure: J.C. Ullery, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 458, 411 (2015), Application(s):Fluorescence microscopy using U937 monocyte and CHO-K1 cell lines, 摘要;
Aflatoxin biosynthesis is a novel source of reactive oxygen species-a potential redox signal to initiate resistance to oxidative stress?: L.V. Roze, et al.; Toxins (Basel). 7, 1411 (2015),Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
Alisertib induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR and sirtuin 1-mediated signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells: F. Wang, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 575 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using PANC-1 and BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Alisertib, an Aurora kinase A inhibitor, induces apoptosis and autophagy but inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human epithelial ovarian cancer: Y.H. Ding, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 425 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using SKOV3 and OVCAR-4 ovarian cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Andrographolide Analogue Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy Mediated Cell Death in U937 Cells by Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway: D. Kumar, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0139657 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometric analysis of Cyto-ID Green Detection Reagent , 摘要; 全文
Apoptotic Cell Death Induced by Resveratrol Is Partially Mediated by the Autophagy Pathway in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: F. Lang, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0129196 (2015),Application(s): Live Cell Imaging, 摘要; 全文
Araguspongine C induces autophagic death in breast cancer cells through suppression of c-Met and HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: M.R. Akl, et al.; Mar. Drugs 13, 288 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using BT-474 breast cancer cell line, 摘要; 全文
Autocrine VEGF maintains endothelial survival through regulation of metabolism and autophagy: C.K. Domigan, et al.; J. Cell. Sci. 128, 2236 (2015), 摘要;
Autophagy is activated in systemic lupus erythematosus and required for plasmablast development: A.J. Clarke, et al.; Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 912 (2015), 摘要; 全文
Autophagy limits proliferation and glycolytic metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia: A.S. Watson, et al.; Cell Death Discov. 1, 15008 (2015), Application(s): CytoID assay in human and mouse HSCs, 摘要; 全文
Baicalin inhibits autophagy induced by influenza A virus H3N2: H.Y. Zhu, et al.; Antiviral Res. 113, 62 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using A549 human lung cancer cell line, 摘要;
Bardoxolone methyl induces apoptosis and autophagy and inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness in esophageal squamous cancer cells: Y.Y. Wang, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 993 (2015), Application(s): Flow Cytometry, 摘要; 全文
Cell-penetrating peptide derived from human eosinophil cationic protein inhibits mite allergen Der p 2 induced inflammasome activation: S.J. Yu, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0121393 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry of THP-1 leukemia cell line, 摘要; 全文
Chemoproteomics Reveals Novel Protein and Lipid Kinase Targets of Clinical CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: N.J. Sumi, et al.; ACS Chem. Biol. 10, 2680 (2015),Application(s): Quantification of autophagosomes, 摘要;
Circulating hemocytes from larvae of the Japanese rhinoceros beetle Allomyrina dichotoma (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and the cellular immune response to microorganisms: S. Hwang, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0128519 (2015), Application(s):Fluorescence microscopy using hemocytes from Japanese rhinoceros beetle Allomyrina dichotoma larvae, 摘要; 全文
Citreoviridin induces ROS-dependent autophagic cell death in human liver HepG2 cells: Y.N. Liu, et al.; Toxicon. 95, 30 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using HepG2 cell line, 摘要;
Clozapine induces autophagic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells: Y.C. Yin, et al.; Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 35, 945 (2015), 摘要;
Coffee and caffeine potentiate the antiamyloidogenic activity of melatonin via inhibition of Aβ oligomerization and modulation of the Tau-mediated pathway in N2a/APP cells: L.F. Zhang, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 241 (2015), Application(s): Flow Cytometry,摘要; 全文
Combination of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001 with temozolomide and radiation effectively inhibits the growth of glioblastoma cells in culture: H. Burckel, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 33, 471 (2015), 摘要;
Danusertib Induces Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Autophagy but Inhibits Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells: D. Zi, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 27228 (2015), Application(s): Confocal fluorescence microscopy, 摘要; 全文
Danusertib, a potent pan-Aurora kinase and ABL kinase inhibitor, induces cell cycle arrest and programmed cell death and inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition involving the PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated signaling pathway in human gastric cancer AGS and NCI-N78 cells: C.X. Yuan, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1293 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using AGS and NCI-N78 gastric cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Defective autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells alters contractility and Ca²⁺ homeostasis in mice: C.F. Michiels, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308, H557 (2015), 摘要;
Effects of cyclodextrins on GM1‐gangliosides in fibroblasts from GM1‐gangliosidosis patients: Y. Maeda, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67, 1133 (2015), 摘要;
Endurance exercise training induces fat depot-specific differences in basal autophagic activity: G. Tanaka, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 466, 512 (2015),Application(s): Detect the formation of autophagosomes, 摘要;
Erbin is a novel substrate of the Sag-βTrCP E3 ligase that regulates KrasG12D-induced skin tumorigenesis: C.M. Xie, et al.; J. Cell. Biol. 209, 721 (2015), 摘要;
Evaluation of Antitumor Effects of Folate-Conjugated Methyl-β-cyclodextrin in Melanoma: K. Motoyama, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38, 374 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence Microscopy, 摘要; 全文
Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1 promotes autophagy during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy: A.C. Laurent, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 105, 55 (2015), Application(s):Fluorescence microscopy using rat neonatal ventricular myocytes, 摘要;
Glutathione-S-transferase omega 1 (GSTO1-1) acts as mediator of signaling pathways involved in aflatoxin B1-induced apoptosis-autophagy crosstalk in macrophages: S. Paul, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 89, 1218 (2015), Application(s): Determination of autophagy with immunocytochemistry , 摘要;
GMI, an immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum, potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis via autophagy in lung cancer cells: I.L. Hsin, et al.; Mol. Pharm. 12, 1534 (2015), 摘要;
Induction of apoptosis and autophagy via sirtuin1- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways by plumbagin in human prostate cancer cells: Z.W. Zhou, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1511 (2015), Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
Induction of autophagy is a key component of all-trans-retinoic acid-induced differentiation in leukemia cells and a potential target for pharmacologic modulation: N. Orfali, et al.; Exp. Hematol. 43, 781 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry analysis of NB4 and HL60 promyelocytic leukemia cell lines, 摘要;
Inhibition of Autophagy Potentiated the Antitumor Effect of Nedaplatin in Cisplatin-Resistant Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells: Z. Liu, et al. ; PLoS One 10, e0135236 (2015),Application(s): Cell culture, 摘要; 全文
Inhibition of mitotic Aurora kinase A by alisertib induces apoptosis and autophagy of human gastric cancer AGS and NCI-N78 cells: C.X. Yuan, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 487 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using AGS and NCI-N78 gastric cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Interferon Regulatory Factor-1 signaling regulates the switch between autophagy and apoptosis to determine breast cancer cell fate: J.L. Schwartz-Roberts, et al.; Cancer Res.75, 1046 (2015), 摘要;
Interplay of Oxidative Stress and Autophagy in PAMAM Dendrimers-Induced Neuronal Cell Death : Y. Li, et al.; Theranostics 5, 1363 (2015), Application(s): Confocal fluorescence assay, 摘要; 全文
Invariant NKT cells require autophagy to coordinate proliferation and survival signals during differentiation: B. Pei, et al.; J. Immunol. 194, 5872 (2015), 摘要;
Involvement of fish signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in nodavirus infection induced cell death: Y. Huang, et al.; Fish Shellfish Immunol. 43, 241 (2015),Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy of Grouper (fish) brain cells, 摘要;
Is the autophagy a friend or foe in the silver nanoparticles associated radiotherapy for glioma?: H. Wu, et al.; Biomaterials 62, 47 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using U251 human glioma cell line, 摘要;
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces Nrf2 activation in latently infected endothelial cells through SQSTM1 phosphorylation and interaction with polyubiquitinated Keap1: O. Gjyshi, et al.; J. Virol. 89, 2268 (2015), 摘要;
KLF4-SQSTM1/p62-associated prosurvival autophagy contributes to carfilzomib resistance in multiple myeloma models: I. Riz, et al.; Oncotarget 6, 17814 (2015), Application(s):FACS, 摘要; 全文
Lithium modulates autophagy in esophageal and colorectal cancer cells and enhances the efficacy of therapeutic agents in vitro and in vivo: T.R. O'Donovan, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0134676 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry analysis using human esophageal and murine colon cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Adaptation to Human Keratinocytes: G. Soong, et al.; MBio. 6, e00289-15 (2015), Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
Mevalonate pathway regulates cell size homeostasis and proteostasis through autophagy: T.P. Miettinen, et al.; Cell Rep. 13, 2610 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry analysis of autophagy using Jurkat, U2OS, Kc167 and HUVEC cells, 摘要;
MiR-29b replacement inhibits proteasomes and disrupts aggresome+autophagosome formation to enhance the antimyeloma benefit of bortezomib: S. Jagannathan, et al.; Leukemia 29, 727 (2015), Application(s): Detection of autophagy by fluorescence microscopy in multiple myeloma cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Molecular chaperone GRP78 enhances aggresome delivery to autophagosomes to promote drug resistance in multiple myeloma: M.A. Abdel Malek, et al.; Oncotarget 6, 3098 (2015), Application(s): Confocal Microscopy, 摘要; 全文
Molecular cloning and characterization of autophagy-related gene TmATG8 in Listeria-invaded hemocytes of Tenebrio molitor: H. Tindwa, et al.; Dev. Comp. Immunol. 51, 88 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using hemocytes from Tenebrio molitor larvae, 摘要;
Molecular pathway of near-infrared laser phototoxicity involves ATF-4 orchestrated ER stress: I. Khan, et al.; Sci. Rep. 5, 10581 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy autophagy assay, 摘要; 全文
N-Myc and STAT Interactor regulates autophagy and chemosensitivity in breast cancer cells: B.J. Metge, et al.; Sci. Rep. 5, 11995 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescent detection,摘要; 全文
Novel autophagy inducers lentztrehaloses A, B and C: S.I. Wada, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)68, 521 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using Mewo melanoma and OVK18 ovarian cancer cell lines, 摘要;
Novel small-molecule SIRT1 inhibitors induce cell death in adult T-cell leukaemia cells: T. Kozako, et al.; Sci. Rep. 5, 11345 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using a variety of cancer cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Novel targeting of PEGylated liposomes for codelivery of TGF-β1 siRNA and four antitubercular drugs to human macrophages for the treatment of mycobacterial infection: a quantitative proteomic study: N. Niu, et al. ; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 4441 (2015),Application(s): Autophagy of human macrophages by flow cytometry, 摘要;
Paraptosis cell death induction by the thiamine analog benfotiamine in leukemia cells: N. Sugimori, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0120709 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using HL60 leukemia cell line, 摘要; 全文
Plumbagin induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells: S.T. Pan, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1601 (2015), Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
Pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38 MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: N.K. Niu, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1555 (2015), Application(s): Assay,摘要; 全文
Reduced FoxO3a expression causes low autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts on collagen matrix: J. Im, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 309, L552 (2015), 摘要;
S-Adenosyl-L-methionine-competitive inhibitors of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 induce autophagy and enhance drug sensitivity in cancer cells: T.P. Liu, et al.; Anticancer Drugs 26, 139 (2015), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line, 摘要; 全文
Schisandrin B inhibits cell growth and induces cellular apoptosis and autophagy in mouse hepatocytes and macrophages: implications for its hepatotoxicity: Y. Zhang, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 2001 (2015), Application(s): Flow cytometry using AML-12 hepatocyte and RAW 264.7 leukemia cell lines, 摘要; 全文
Src/STAT3-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction mediates chemoresistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by promoting autophagy: Q. Tan, et al.; Cancer Sci. 106, 1023 (2015), 摘要;
The CCL2 chemokine is a negative regulator of autophagy and necrosis in luminal B breast cancer cells: W.B. Fang, et al.; Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 150, 309 (2015), 摘要;
The investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) induces cell cycle G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells: J.P. Li, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1627 (2015),Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
The pan-inhibitor of Aurora kinases danusertib induces apoptosis and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells: J.P. Li, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 1027 (2015), Application(s): Assay, 摘要; 全文
The role of autophagy in the cytotoxicity induced by recombinant human arginase in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: C. Lin, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99, 8487 (2015), 摘要;
A Novel CXCR3-B Chemokine Receptor-induced Growth-inhibitory Signal in Cancer Cells Is Mediated through the Regulation of Bach-1 Protein and Nrf2 Protein Nuclear Translocation : M. Balan & S. Pal; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 3126 (2014), Application(s): Monitor autophagy in MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cells by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy, 摘要;
Adaptive responses to glucose restriction enhance cell survival, antioxidant capability, and autophagy of the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis: K.Y. Huang, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1840, 53 (2014), 摘要;
Autophagy in the brain of neonates following hypoxia-ischemia shows sex-and region-specific effects: S.N. Weis, et al.; Neuroscience 256, 201 (2014), 摘要;
Cannabinoid-induced autophagy regulates suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in intestinal epithelium: L.C. Koay, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 307, G140 (2014),Application(s): Detection of autophagy in human colonic epithelial cell line Caco-2 by Confocal imaging, 摘要; 全文
Caveolin-1 Is a Critical Determinant of Autophagy, Metabolic Switching, and Oxidative Stress in Vascular Endothelium: T. Shiroto, et al.; PLoS One 9, e87871 (2014), 摘要;全文
Connective tissue diseases: How do autoreactive B cells survive in SLE-autophagy?: N.J. Bernard; Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 10, 128 (2014), (Review), 摘要;
Defective Autophagosome Trafficking Contributes to Impaired Autophagic Flux in Coronary Arterial Myocytes Lacking CD38 Gene: Y. Zhang, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 102, 68 (2014),摘要;
Defects in mitochondrial clearance predispose human monocytes to interleukin-1β hyper-secretion: R. van der Burgh, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 5000 (2014), 摘要; 全文
Early biomarkers of response to carfilzomib in multiple myeloma (MM): Modulation of CXCR4 and induction of autophagy: M. Bhutani, et al.; J. Clin. Oncol. 32, e19572 (2014),Application(s): Quantification of autophagy in malignant plasma cells from bone marrow aspirates by flow cytometry with the Cyto-ID autophagy detection kit,
Enhancement of dynein-mediated autophagosome trafficking and autophagy maturation by ROS in mouse coronary arterial myocytes: M. Xu, et al.; J. Cell. Mol. Med. 18, 2165 (2014), 摘要; 全文
Flow Cytometric Analysis of Autophagic Activity with Cyto-ID Staining in Primary Cells: M. Stankov, et al.; Bio-Protocol (2014), Application(s): FC in primary BMDCs, 全文
High-Content Assays for Hepatotoxicity Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cells: O. Sirenko, et al.; Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 12, 43 (2014), 摘要; 全文
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce apoptosis in myeloid leukemia by suppressing autophagy: M.V. Stankov, et al.; Leukemia 28, 577 (2014), 摘要;
Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate VSV oncolysis in prostate cancer cells by modulating NF-κB dependent autophagy: L. Shulak, et al.; J. Virol. 88, 2927 (2014),摘要;
In vitro and in vivo characterization of porcine acellular dermal matrix for gingival augmentation procedures: A.M. Pabst, et al.; J. Periodontal. Res. 49, 371 (2014), 摘要;
Inhibition of Autophagic Flux by Salinomycin Results in Anti-Cancer Effect in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: J. Klose, et al.; PLoS One 9, e95970 (2014),Application(s): Autophagy detection in human hepatocellular carcinoma , 摘要; 全文
Inhibition of stress induced premature senescence in presenilin-1 mutated cells with water soluble Coenzyme Q10: D. Ma, et al.; Mitochondrion 17C, 106 (2014), Application(s):Autophagic vacuoles in Alzheimer's Disease fibroblasts detected with CytoID® Green Autophagy Detection kit, 摘要;
Involvement of autophagy in recombinant human arginase-induced cell apoptosis and growth inhibition of malignant melanoma cells: Z. Wang, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.98, 2485 (2014), 摘要;
MiR-216a: a link between endothelial dysfunction and autophagy: R. Menghini, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1029 (2014), 摘要;
Novel estradiol analogue induces apoptosis and autophagy in esophageal carcinoma cells: E. Wolmarans, et al.; Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 19 , 98 (2014), Application(s): Autophagy detection in esophageal carcinoma SNO cell , 摘要;
Novel sorafenib-based structural analogues: in-vitro anticancer evaluation of t-MTUCB and t-AUCMB: A.T. Wecksler, et al.; Anticancer Drugs 25, 433 (2014), 摘要;
Photodynamic therapy with the novel photosensitizer chlorophyllin f induces apoptosis and autophagy in human bladder cancer cells: D. Lihuan, et al.; Lasers Surg. Med. 46, 319 (2014), 摘要;
Plumbagin induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cells: Y.C.Li, et al.; Cancer Lett. 344, 239 (2014), 摘要;
Potential of adenovirus-mediated REIC/Dkk-3 gene therapy for use in the treatment of pancreatic cancer: D. Uchida, et al.; J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 29, 973 (2014), 摘要;
Sirt1 modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy in heart: A. Guilbert, et al.; Cardiovasc. Res. 103 (suppl 1), S13 (2014), Application(s): Evaluation of Autophagy in H9c2 cells, rat cardiomyoblasts by flow cytometry, 全文
STAT3 down regulates LC3 to inhibit autophagy and pancreatic cancer cell growth: J. Gong, et al.; Oncotarget 5, 2529 (2014), Application(s): Autophagic vacuole formation was detected by microscopy and autophagosome formation was determined by flow cytometry in human pancreatic cancer cells Capan-2, 摘要; 全文
T-Cell Autophagy Deficiency Increases Mortality and Suppresses Immune Responses after Sepsis: C.W. Lin, et al.; PLoS One 9, e102066 (2014), Application(s): Quantification of autophagosomes and autolysosomes staining in CD4+ and CD8+ cell population by flow cytometry , 摘要; 全文
Tetracyclines cause cell stress-dependent ATF4 activation and mTOR inhibition: A. Brüning, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 320, 281 (2014), 摘要;
The core autophagy protein ATG4B is a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in CML stem/progenitor cells: K. Rothe, et al.; Blood 123, 3622 (2014), Application(s): Monitor autophagy flux in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, 摘要;
Androgen deprivation and androgen receptor competition by bicalutamide induce autophagy of hormone-resistant prostate cancer cells and confer resistance to apoptosis: B. Boutin, et al.; Prostate 73, 1090 (2013), Application(s): Measurement of autophagic flux in prostate cancer cells, 摘要;
Arenobufagin, a natural bufadienolide from toad vonem, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: D.M. Zhang, et al.; Carcinogenesis 34, 1331 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection in hepatocellular carcinoma, 摘要;
Autophagy Plays a Critical Role in ChLym-1-Induced Cytotoxicity of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Cells: J. Fan, et al.; PLoS One. 8, e72478 (2013), 摘要; 全文
BCL-2 inhibitors sensitize therapy-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to VSV oncolysis: S. Samuel, et al.; Mol. Ther. 21, 1413 (2013), 摘要;
Bleomycin exerts ambivalent antitumor immune effect by triggering both immunogenic cell death and proliferation of regulatory T cells: H. Bugaut, et al.; PLoS One 8, e65181 (2013),Application(s): Measurement of autophagy by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy, 摘要; 全文
Celecoxib enhances radiosensitivity of hypoxic glioblastoma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress: K. Suzuki, et al.; Neuro. Oncol. 15, 1186 (2013), 摘要;
Chloroquine Engages the Immune System to Eradicate Irradiated Breast Tumors in Mice: J.A. Ratikan, et al.; Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 87, 761 (2013), 摘要;
Dietary Resveratrol Prevents Development of High-Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplastic Lesions: Involvement of SIRT1/S6K Axis: G. Li, et al.; Cancer Prev. Res 6, 27 (2013), Application(s): Effects of Resveratrol on prostate tumorigenesis, 摘要;
Enhancement of autophagy by simvastatin through inhibition of Rac1-mTOR signaling pathway in coronary arterial myocytes: Y.M. Wei, et al.; Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 31, 925 (2013), 摘要; 全文
GX15-070 (obatoclax) induces apoptosis and inhibits cathepsin D and L mediated autophagosomal lysis in antiestrogen resistant breast cancer cells: J.L. Schwartz-Roberts, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 12, 448 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection in breast cancer cells, 摘要;
Hydroxychloroquine preferentially induces apoptosis of CD45RO+ effector T cells by inhibiting autophagy: A possible mechanism for therapeutic modulation of T cells: J. van Loodregt, et al.; J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 131, 1443 (2013), Application(s): Detection of autophagy in CD4+ T cells and PBMC by flow cytometry , 摘要; 全文
Interactions between autophagic and endo-lysosomal markers in endothelial cells: C.L. Oeste, et al.; Histochem. Cell. Biol. 139, 659 (2013), 摘要;
Involvement of cholesterol depletion from lipid rafts in apoptosis induced by methyl-β-cyclodextrin: R. Onodera, et al.; Int. J. Pharm. 452, 116 (2013), Application(s):Measurement of autophagy by fluorescence microscopy, 摘要;
ISG15 deregulates autophagy in genotoxin-treated ataxia telangiectasia cells: S.D. Desai, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 288, 2388 (2013), Application(s): Fluorescence microscopy using Ataxia Telangiectasia cells, 摘要; 全文
Lysosomal basification and decreased autophagic flux in oxidatively stressed trabecular meshwork cells: Implications for glaucoma pathogenesis: K. Porter, et al.; Autophagy 9, 581 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection by flow cytometry in porcine TM cells,摘要; 全文
Nelfinavir and bortezomib inhibit mTOR activity via ATF4-mediated sestrin-2 regulation: A. Brüning; Mol. Oncol. 7, 1012 (2013), 摘要;
Recombinant human arginase induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and autophagy in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cells: X. Zeng, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e840 (2013), 摘要;全文
Regulation of autophagic flux by dynein-mediated autophagosomes trafficking in mouse coronary arterial myocytes: M. Xu, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1833, 3228 (2013),摘要;
Renal cancer-selective Englerin A induces multiple mechanisms of cell death and autophagy: R.T. Williams, et al.; J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 32, 57 (2013), Application(s):Flow cytometry and immunofluorescence of a human kidney carcinoma cell line, 摘要;全文
Saxifragifolin D induces the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells through ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress: J.M. Shi, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 85, 913 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection by flow cytometry in breast cancer cells, 摘要;
Suppression of autophagy enhanced growth inhibition and apoptosis of interferon-β in human glioma cells: Y. Li, et al.; Mol. Neurobiol. 47, 1000 (2013), 摘要;
Survival and death strategies in glioma cells: autophagy, senescence and apoptosis triggered by a single type of temozolomide-induced DNA damage: A.V. Knizhnik, et al.; PLoS One 8, e55665 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection by flow cytometry in glioma cells, 摘要; 全文
The effect of Zhangfei on the unfolded protein response and growth of cells derived from canine and human osteosarcomas: T. Bergeron, et al.; Vet. Comp. Oncol. 11, 140 (2013),Application(s): Detection of autophagy in human and canine osteosarcoma, 摘要;
The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 potentiates autophagic cell death induced by temozolomide in a glioblastoma cell line: E. Josset, et al.; Anticancer Res. 33, 1845 (2013), 摘要;
Therapeutic Combination of Nanoliposomal Safingol and Nanoliposomal Ceramide for Acute Myeloid Leukemia: T.J. Brown, et al.; J. Leuk. 1, 110 (2013), Application(s):Detection of autophagy by flow cytometry in Human HL-60 , HL-60/VCR, and murine C1498 cells, 全文
Type I interferons induce autophagy in certain human cancer cell lines: H. Schmeisser, et al.; Autophagy 9, 683 (2013), Application(s): Autophagy detection in type I interferon-treated human cancer cell lines, 摘要;
A novel image-based cytometry method for autophagy detection in living cells: L.L. Chan, et al.; Autophagy 8, 1371 (2012), 摘要; 全文
Apoptosis and autophagy have opposite roles on imatinib-induced K562 leukemia cell senescence: C. Drullion, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 3, e373 (2012), Application(s): Flow cytometry of human CML cells treated with Imatinib, 摘要; 全文
Counteracting autophagy overcomes resistance to everolimus in mantle cell lymphoma: L. Rosich, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 5278 (2012), 摘要; 全文
Heme Oxygenase-1 Promotes Survival of Renal Cancer Cells through Modulation of Apoptosis-and Autophagy-regulating Molecules: P. Banerjee, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 287, 4962 (2012), Application(s): Detection of autophagy in human renal cancer cells, 摘要;
Inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter 2 induces senescence-associated mitochondrial dysfunction and suppresses progression of colorectal malignancies in vivo: I. Lee, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 11, 2342 (2012), 摘要; 全文
Mechanism for the induction of cell death in ONS-76 medulloblastoma cells by Zhangfei/CREB-ZF: T.W. Bodnarchuk, et al.; J. Neurooncol. 109, 485 (2012),Application(s): Detection of autophagy in medulloblastoma cells, 摘要;
Mitochondrial metabolism in Parkinson's disease impairs quality control autophagy by hampering microtubule-dependent traffic: D.M. Arduíno, et al.; Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 4680 (2012), 摘要; 全文
Proteasome inhibition by quercetin triggers macroautophagy and blocks mTor activity: A.K. Klappan, et al.; Histochem. Cell Biol. 137, 25 (2012), 摘要;
Reovirus as a viable therapeutic option for the treatment of multiple myeloma: C.M. Thirukkumaran, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 4962 (2012), Application(s): Detection of autophagy in human myeloma cell lines and ex vivo tumor specimens, 摘要;
Src inhibition with saracatinib reverses fulvestrant resistance in ER-positive ovarian cancer models in vitro and in vivo: F.A. Simpkins, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 5911 (2012),Application(s): Detection of autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells and xenografts,摘要;
FoxM1 knockdown sensitizes human cancer cells to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis but not to autophagy: B. Pandit, et al.; Cell Cycle 10, 3269 (2011), Application(s):Flow cytometry using human cancer cells, 摘要; 全文
Monitoring of autophagy in Chinese hamster ovary cells using flow cytometry: J.S. Lee, et al.; Methods 56(3), 375 (2011), 摘要;
Selective anticancer activity of a hexapeptide with sequence homology to a non-kinase domain of Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4: H.M. Warenius, et al.; Mol. Cancer 10, 72 (2011),摘要;
Silibinin triggers apoptotic signaling pathways and autophagic survival response in human colon adenocarcinoma cells and their derived metastatic cells: H. Kauntz, et al.; Apoptosis16, 1042 (2011), 摘要;